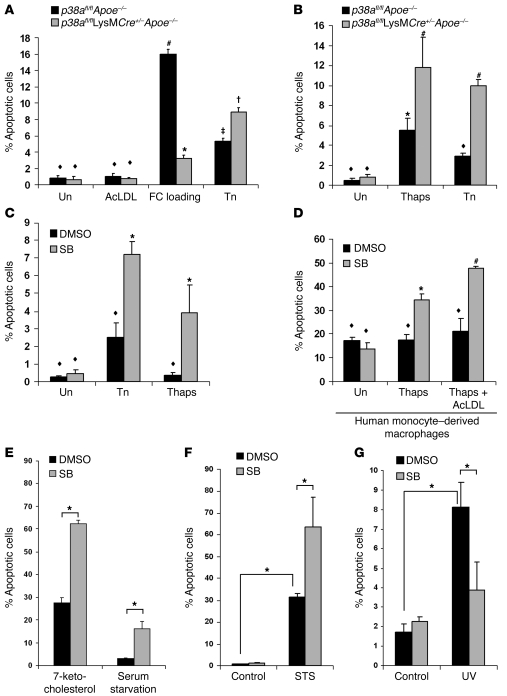
Figure 6. Inhibition of p38α MAPK accelerates macrophage apoptosis during ER stress.
(A) p38afl/flApoe–/– and p38afl/flLysMCre+/–Apoe–/– peritoneal macrophages were left untreated (Un), treated with acetyl-LDL (AcLDL), cholesterol-loaded (acetyl-LDL plus 58035; FC loading) for 16–18 h, or treated with 5 μg/ml tunicamycin (Tn) for 24 h, after which cells were assayed for apoptosis. Data are expressed as the percent of total cells that stained with annexin V and propidium iodide. (B) Cells as in A were untreated or treated with 2 μM thapsigargin (Thaps) or 5 μg/ml tunicamycin for 24 h, then assayed as in A. (C and D) Wild-type mouse peritoneal (C) or human monocyte–derived (D) macrophages were pretreated with 10 μM SB202190 (SB) or the vehicle DMSO control for 1 h and then treated with 5 μg/ml tunicamycin or 0.25 μM thapsigargin (C) or with 0.25 μM thapsigargin or 0.25 μM thapsigargin plus acetyl-LDL (D) for 24 h and assayed for apoptosis as described in A. In A–D, common symbols denote differences that are not statistically significant (P > 0.05), while different symbols denote statistically significant differences (P < 0.05); ANOVA with Student-Newman-Keuls post-test. (E–G) Peritoneal macrophages were pretreated for 1 h with 10 μM SB202190 or the vehicle DMSO control. Cells were then given 20 μg/ml 7-ketocholesterol or serum starved for 18 h (E), treated with 100 nM staurosporine (STS) for 24 h (F), or UV irradiated and followed for 7 h (G). Cells were then assayed for apoptosis as described in A. All data are mean ± SEM (n = 4). In E–G, *P < 0.05, ANOVA with Student-Newman-Keuls post-test.