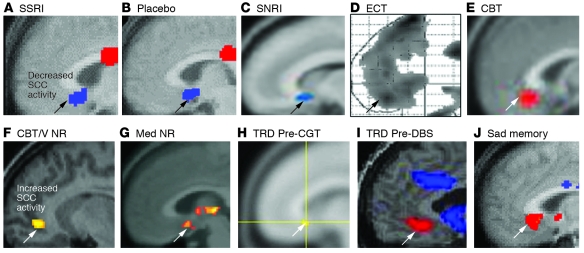
Figure 3. Converging evidence implicating the SCC region in MDD.
(A–E) Common pattern of changes in glucose metabolism or blood flow in the SCC with antidepressant response to various interventions. Images demonstrate group change patterns relative to the baseline depressed state for each treatment: (A) metabolic decreases with the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) fluoxetine; (B) metabolic decreases with a placebo pill; (C) metabolic decreases with the serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) venlafaxine; (D) blood flow decreases with ECT; and (E) metabolic increases with CBT. (F–J) Images demonstrate elevated resting-state SCC25 activity in various groups of patients with TRD: (F) metabolic increases in CBT and venlafaxine (V) nonresponders (NRs) relative to both healthy subjects and similarly depressed patients who responded to either treatment; (G) resting-state fMRI increases in pharmacotherapy (Med) nonresponders relative to healthy controls; (H) glucose metabolic increases in patients with TRD who later responded to cingulotomy (CGT) relative to those that failed to respond; (I) blood flow increases in patients with TRD, enrolled in a DBS treatment trial relative to healthy controls; (J) SCC blood flow increases with induction of transient sadness induced by recollection of a personal sad memory in healthy subjects, a pattern similar to that seen in patients with TRD. Red indicates increased activity (white arrows) and blue indicates decreased activity (black arrows). Images are courtesy of Mitch Nobler (D), Michael Greicius (G), and Darin Dougherty (H). Panels A and J are generated from data published in American Journal of Psychiatry (10). Panels B and D are adapted with permission from American Journal of Psychiatry (refs. 79 and 73, respectively). Panel I is adapted with permission from Neuron (11). Panels C and E are adapted with permission from American Journal of Psychiatry (62). Panel F is generated from data published in American Journal of Psychiatry (62). Panel G is adapted with permission from Biological Psychiatry (68). Panel H is adapted with permission from Journal of Neurosurgery (66).