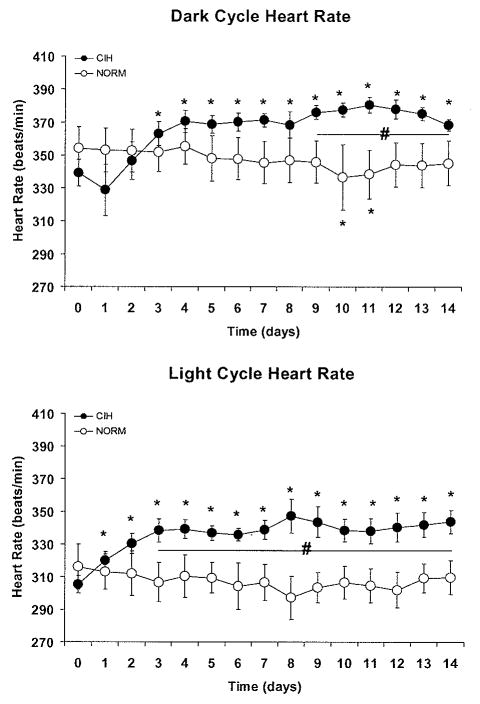
Figure 4.
Exposure to chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH) produced increases in heart rate above baseline that were evident during the dark cycle (top panel), when intermittent hypoxic cycles occurred, and also during the light cycle (bottom panel), when the animals were unperturbed. *P<0.05 vs. baseline value, # P<0.05 for CIH vs. NORM. Data points were computed as described in Figure 3.