Figure 6.
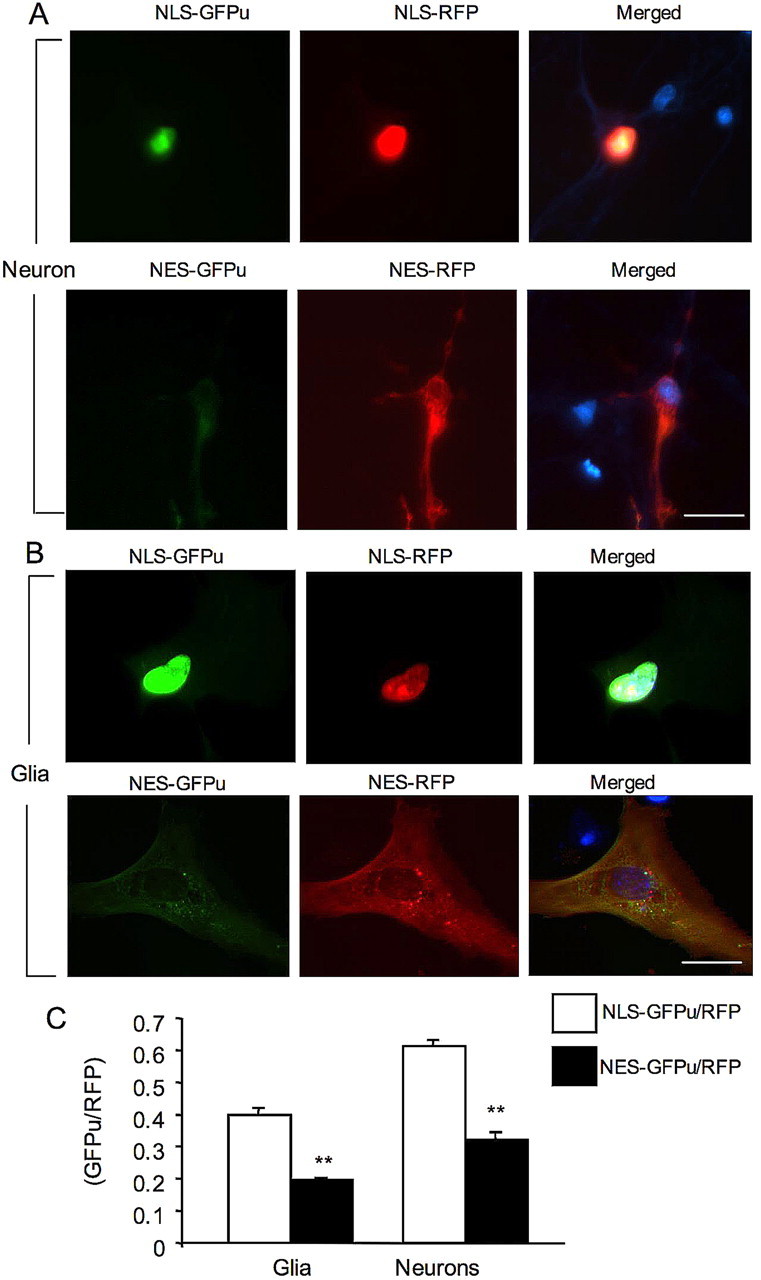
Targeting GFPu/RFP to the nucleus and cytoplasm of cultured cells. A, NLS–GFPu/RFP (top) or NES–GFPu/RFP (bottom) were transfected into cultured rat brain cortical neurons at 8 DIV. Note that nuclear NLS–GFPu is more intense than cytoplasmic NES–GFPu. B, Cultured astrocytes at 20 DIV were infected with adenoviral NLS–GFPu/RFP (top) or NES–GFPu/RFP (bottom). Note that nuclear NLS–GFPu signal is also more intense than cytoplasmic NES–GFPu. In A and B, merged images show the Hoechst-stained nuclei (blue). Scale bars, 10 μm. C, Quantification of the ratios (mean + SEM, n = 10–16) for NLS–GFPu/RFP in the nucleus and NES–GFPu/RFP in the cytoplasm in glia and neurons. **p < 0.01.
