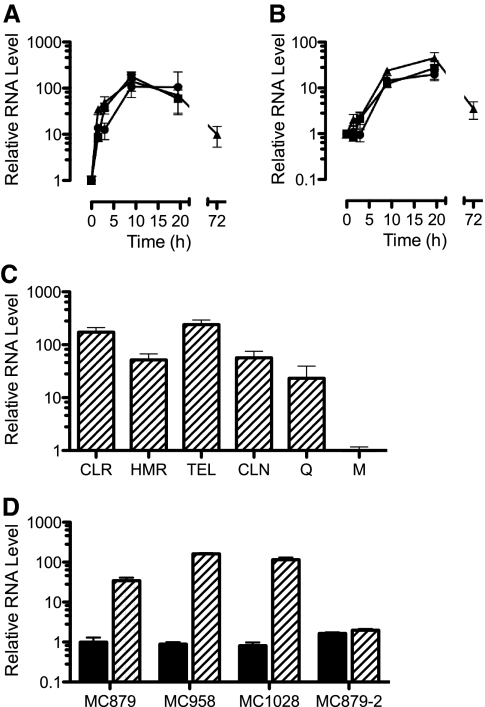
FIG. 4.
RNA levels, relative to the baseline (time zero), for erm(41) (A) and coaE (B) in M. abscessus isolate MC879 after addition of clarithromycin at 0.1 μg/ml (triangle) or 1 μg/ml (circle) or erythromycin at 0.1 μg/ml (square). (C) Relative erm(41) RNA levels for isolate MC879 incubated for 24 h in clarithromycin (CLR; 1 μg/ml), HMR3004 (HMR; 1 μg/ml), telithromycin (TEL; 32 μg/ml), clindamycin (CLN; 128 μg/ml), or quinupristin (Q; 128 μg/ml); RNA levels are relative to those for organisms incubated in medium alone (M). (D) erm(41) RNA levels at the baseline (shaded bars) and after 24 h of incubation with erythromycin at 0.1 μg/ml (hatched bars) for four isolates of M. abscessus. All levels are relative to the baseline erm(41) RNA level of isolate MC879. Isolate MC1028 had a nonfunctional erm(41) allele, and isolate MC879-2 had a functional erm(41) allele but carried a 23S rRNA gene mutation conferring constitutively high-level macrolide resistance.