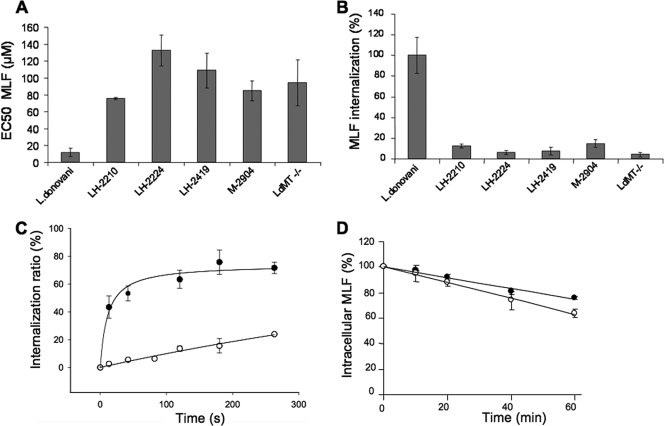
FIG. 1.
L. braziliensis strains are less sensitive to MLF and have less drug internalization than L. donovani. (A) MLF sensitivity of promastigotes of the L. donovani wild-type and LdMT−/− lines and L. braziliensis strains LH-2210, LH-2224, LH-2419, and M-2904. Shown are EC50s after 72 h of culture. The results shown are the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. (B) [14C]MLF internalization into promastigotes of the L. donovani wild-type and LdMT−/− lines and L. braziliensis strains LH-2210, LH-2224, LH-2419, and M-2904. Internalization was measured after 60 min of incubation at 28°C and expressed as a percentage of the internalization by wild-type L. donovani. Bars represent the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. (C) Initial rate of [14C]MLF internalization in promastigotes of the L. donovani wild-type (black circles) and L. braziliensis LH-2419 (open circles) strains. The data are expressed as the percentage of [14C]MLF inside the cells with respect to the drug bound to the outer leaflet of the PM at the indicated time points. Each point represents the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. (D) [14C]MLF efflux. Promastigotes of the L. donovani wild-type (black circles) and L. braziliensis LH-2419 (white circles) strains were preincubated with [14C]MLF at 28°C, and the decay in radioactivity was monitored at different times (10, 20, 40, and 60 min). The data are expressed as the percentage of the initial amount of [14C]MLF incorporated. Each point represents the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments.