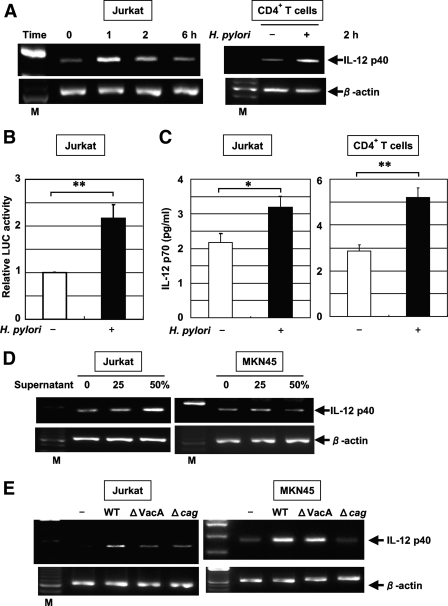
FIG. 7.
H. pylori-induced IL-12 p40 mRNA expression in T cells. (A) Total RNA was extracted from Jurkat cells and CD4+ T cells infected with H. pylori ATCC 49503 for the indicated times and used for RT-PCR (MOI, 10). M, size marker. (B) H. pylori activates the IL-12 p40 promoter in T cells. The IL-12 p40 reporter construct was transfected into Jurkat cells, and subsequently the cells were infected with H. pylori ATCC 49503 for 6 h (MOI, 20). The activity is expressed relative to that of cells transfected with the construct without further H. pylori infection, which was defined as 1. Data are means ± standard deviations from three independent experiments. **, P < 0.01, as determined by the Student t test. LUC, luciferase. (C) Increased secretion of IL-12 p70 into the supernatants of Jurkat and CD4+ T-cell cultures in response to H. pylori ATCC49503 infection at 24 h. IL-12 p70 concentrations in the supernatants were determined by ELISA. Data are means ± standard deviations from three experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; both were determined by the Student t test. (D) Jurkat and MKN45 cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of culture supernatants from H. pylori ATCC 49503 for 2 h. Note the supernatant-induced IL-12 p40 mRNA expression in Jurkat cells but not in MKN45 cells. (E) VacA and the cag PAI of H. pylori are required for the induction of IL-12 p40 expression in Jurkat cells, but VacA is not essential for the induction of IL-12 p40 in MKN45 cells. Total RNA was extracted from Jurkat and MKN45 cells infected with H. pylori (wild-type [WT] strain 26695 or the isogenic mutants ΔVacA and Δcag PAI) for 2 h and used for RT-PCR. Representative results from three similar experiments are shown in each panel.