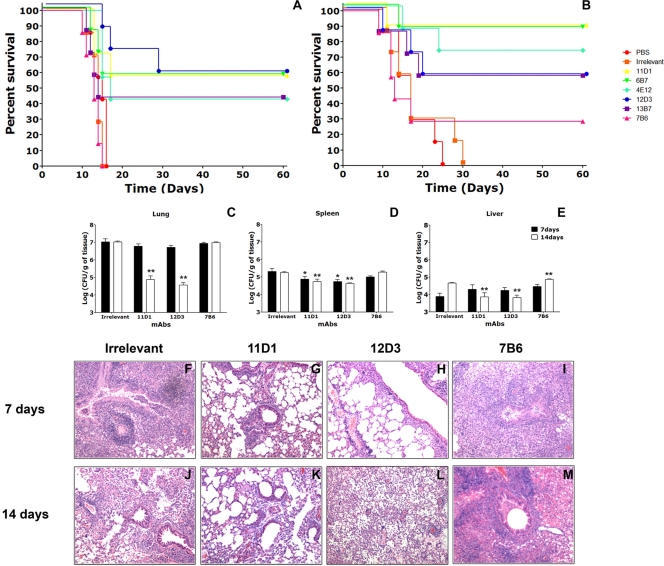
FIG. 5.
MAbs to Hsp60 affect the pathogenesis of histoplasmosis. (A) Intraperitoneal injection of 500 μg of IgG1 (11D1 and 6B7) or IgG2a (4E12, 12D3, and 13B7) MAbs 2 h prior to infection significantly prolonged survival (P < 0.05 for a comparison to controls), but injection of IgG2b MAb 7B6 did not prolong survival. (B) IgG1 and IgG2a MAbs were protective when they were preincubated with H. capsulatum var. capsulatum yeast cells prior to infection (P < 0.05), and the IgG2b MAb was not protective. Each panel shows survival results representative of three similar experiments. (C to E) Numbers of CFU in (C) lungs, (D) spleens, and (E) livers at 7 and 14 days after sublethal intranasal challenge with 5 × 106 H. capsulatum var. capsulatum yeast cells for mice treated intraperitoneally with selected MAbs to Hsp60 or an irrelevant MAb. *, P < 0.001 at 7 days postinfection; **, P < 0.001 at 14 days postinfection. (F to M) IgG1 and IgG2a MAbs to Hsp60 decrease inflammation and the fungal burden in tissues. (F to I) Lung sections obtained after 7 days of infection; (J to M) lung sections obtained after 14 days of infection. The lungs of mice treated with protective MAbs 11D1 and 12D3 exhibited peribronchiolar inflammation at day 7 (G and H, respectively) and resolving inflammation at day 14 (K and L, respectively). In contrast, sections of lungs from the control group and MAb 7B6-treated animals exhibited diffuse, dense inflammation with increased tissue infiltration and early granuloma formation at 7 days (I). Although in the lungs of control mice there was evidence of reduced inflammation at day 14 (J), mice treated with MAb 7B6 had progressive necrotizing pneumonia (M).