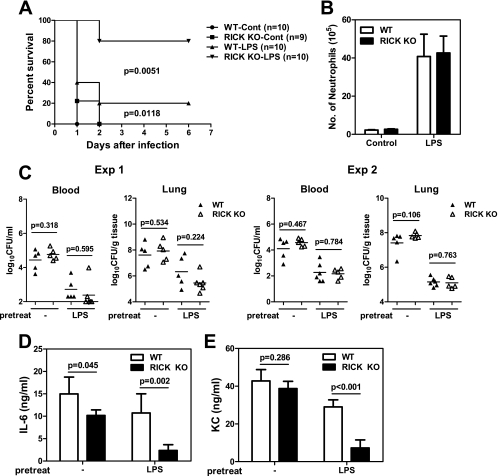
FIG. 6.
RICK contributes to lethality after intraperitoneal P. aeruginosa infection in mice stimulated with LPS. (A) Wild-type (WT) and RICK-deficient (RICK knockout [KO]) mice were injected i.p. with PBS (control [Cont]) or LPS (10 μg/animal) once a day for two days and infected with P. aeruginosa 2 × 107 CFU/animal 24 h after the second LPS injection. Lethality was monitored for more than 6 days after infection. The results from two experiments were pooled together. (B) Neutrophil (GR1+/7/4+) recruitment was assessed at 48 h in peritoneal fluid samples from WT and RICK-deficient mice injected with PBS or LPS twice as in panel A, in the absence of P. aeruginosa infection. (C to E) Mice were treated with PBS or LPS as in panel A and infected with P. aeruginosa (2 × 107 CFU/animal). (C) Bacterial loads in blood and lung samples were determined at 8 h postinfection in two separate experiments. The short black horizontal lines show the mean values for the groups. Each symbol shows the value for one animal. (D and E) At 3 h postinfection, the levels of IL-6 (D) and KC (E) in serum were assessed by ELISAs.