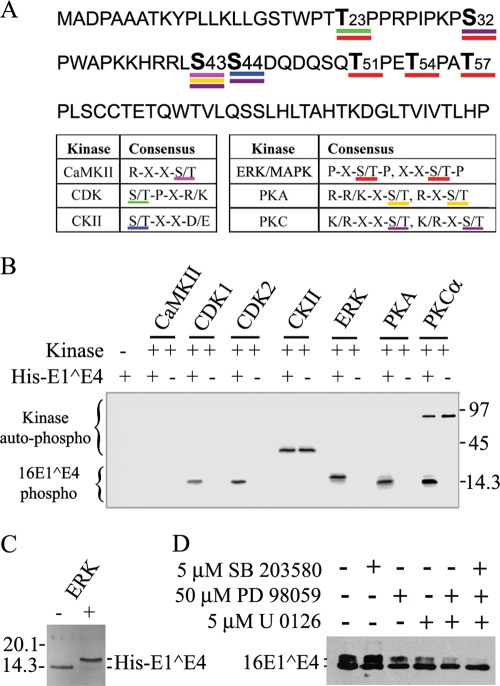
FIG. 2.
16E1^E4 protein is phosphorylated by multiple kinases, with ERK stimulating a gel shift. (A) Putative phosphorylation sites of 16E1^E4 based on common kinase consensus sites are shown. (B) His-16E1^E4 was used as a substrate in kinase assays with [γ-32P]ATP and CDK1, CDK2, CKII, ERK, PKA, or PKC α. Samples were separated by SDS-PAGE, and then phosphorylation was detected using a phosphorimager. His-16E1^E4 was phosphorylated by CDK1, CDK2, ERK, PKA, and PKC α. Autophosphorylation (auto-phospho) of the kinase is apparent in the CKII and PKC α lanes. Molecular mass standards (in kilodaltons) are shown to the right. 16E1^E4 phospho, phosphorylated 16E1^E4; +, present; −, absent. (C) His-16E1^E4 was incubated with or without ERK under kinase assay conditions and then analyzed by silver staining. 16E1^E4 phosphorylation by ERK caused a gel shift. Molecular mass standards (in kilodaltons) are shown to the left. (D) rAd16E1^E4-infected SiHa cells were incubated with the kinase inhibitors SB203580, PD98059, and U0126 (separately or in combination) 6 h postinfection. Cells were harvested 24 h postinfection, and extracts were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-16E1^E4 antibody. The MEK inhibitors PD98059 and/or U0126 reduced the intensity of the upper 16E1^E4 band.