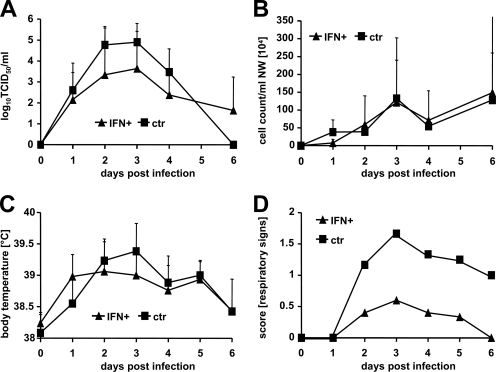
FIG. 2.
HuIFN-αB/D reduces respiratory signs after influenza A virus challenge. Groups of six animals were treated intranasally with 107 U of E. coli-produced IFN-αB/D in a volume of 250 μl of supernatant at 20 and 4 h before infection and at 24 h post-intranasal infection with 105 TCID50 of the H3N2 strain PC/73. The control animals were not treated. (A) Virus titers in nasal washes; (B) nasal wash (NW) cell counts; (C) body temperature. Group averages at the indicated time points are shown. Error bars represent standard deviations. (D) Respiratory signs. Sneezing, nose exudates, and congestion were graded on a 0-1-2 scale, with 0 indicating minimal deviation of the physiologic state; 1 indicating moderate nasal discharge, congestion, and/or occasional sneezing; and 2 indicating severe nasal discharge and/or labored breathing, dyspnea, and frequent sneezing. Group averages are shown.