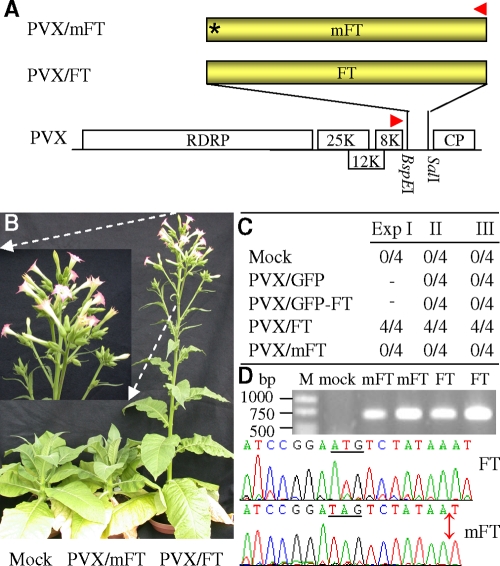
FIG. 3.
Ectopic expression of FT induces flowering. (A) The translatable and mutated (*) nontranslatable Arabidopsis FT coding sequences were cloned into wild-type PVX vector to produce PVX/FT and PVX/mFT, respectively. (B and C) Floral induction caused by viral expression of FT protein. Young SD N. tabacum Maryland Mammoth plants were mock inoculated or infected with PVX/FT or PVX/mFT and grown under a noninducing LD photoperiod. Twelve plants infected by PVX/FT in three separate experiments started bolting at ∼20 dpi, flowered at ∼35 dpi, and were photographed at 42 dpi (B and inset image). Tobacco mock inoculated or infected with PVX/mFT, PVX/GFP, or PVX/GFP-FT did not flower (B and C). (D) Detection of viral transient FT RNA. Viral transient FT RNA was detected by RT-PCR using primers PP82 (▸) and PP356 (◂) in systemic young leaves from two separate plants infected with PVX/mFT (mFT) or PVX/FT (FT) but not in a mock-infected plant (mock). The position and the sizes of 1-kb DNA ladder (lane M) are indicated. Direct sequencing of RT-PCR products (648 bp) verified the presence of virally expressed wild-type and mutant FT RNA in flowering and nonflowering plants, respectively. The native FT ATG (underlined) in PVX/FT and its TAG replacement (underlined) together with a nucleotide deletion (double-arrow) in PVX/mFT are indicated.