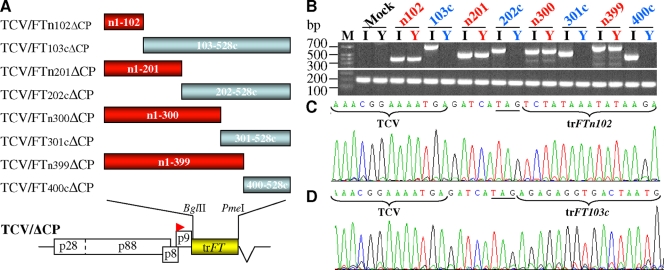
FIG. 5.
Functional mapping of the cis-acting element that controls the FT RNA movement. (A) TCV/trFTΔCP-based RMA vectors carrying truncated (tr) nontranslatable Arabidopsis FTs. (B) Detection of virus-derived FT RNA (top panel) by RT-PCR in systemic young leaves (Y) from plants inoculated with TCV/FTn102ΔCP (n102), TCV/FTn201ΔCP (n201), TCV/FTn300ΔCP (n300), or TCV/FTn399ΔCP (n399); but not from plants inoculated with TCV/FT103cΔCP (103c), TCV/FT202cΔCP (202c), TCV/FT301cΔCP (301c) or TCV/FT400cΔCP (400c). Recombinant viral RNA of each TCV/trFTΔCP was readily detectible in inoculated leaves (I). No specific virus-derived FT RNA was detected in mock-inoculated plants. RT-PCR analysis of 18S rRNA (bottom panel) is included as an RNA control. (C and D) Direct sequencing of RT-PCR products verified the presence of virus-derived truncated FT RNA. Example sequence panels are shown for truncated FT RNA expressed in the young leaves of plants inoculated by TCV/FTn102ΔCP (C) or in the TCV/FT103cΔCP-inoculated leaves (D). The TAG stop codon is underlined and TCV and virus-derived FT sequences are indicated.