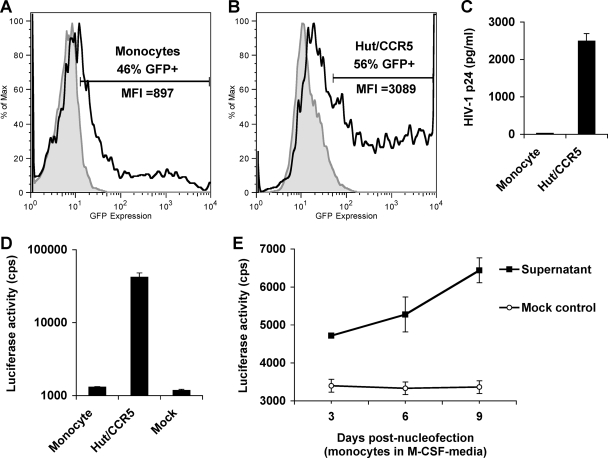
FIG. 3.
Nucleofection of monocytes with HIV-1 proviral DNA cannot produce infectious HIV-1, while macrophage differentiation stimulates HIV-1 production. (A and B) Freshly isolated monocytes (A) and Hut/CCR5 cells (B) were nucleofected with pmax-GFP. GFP expression was measured 24 h postnucleofection by flow cytometry. Filled gray peaks represent mock-transfected controls; open peaks defined by bold lines represent GFP-positive cells. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity (x axes). y axes represent relative cell numbers. (C) Undetectable HIV-1 p24 in the supernatants of monocytes nucleofected with HIV-1 proviral DNA. Primary monocytes and Hut/CCR5 cells were nucleofected with HIV-1 proviral DNA pNLAD8. Gag p24 levels in the supernatants of transfected cells were measured at 3 days posttransfection. (D and E) HIV-1 indicator TZM-bl cells were infected with the supernatants derived from pNLAD8-nucleofected cells. Medium was used as a mock control of the infection. Infected TZM-bl cells were lysed at 5 dpi for the detection of luciferase activity. (D) Undetectable HIV-1 infectivity in the supernatants of pNLAD8-nucleofected monocytes. Supernatants of pNLAD8-nucleofected Hut/CCR5 cells were used as a positive control. (E) Macrophage differentiation stimulates HIV-1 production of monocytes transfected with proviral DNA. Primary monocytes were nucleofected with pNLAD8 and then cultured in the presence of M-CSF. At 3, 6, and 9 days postnucleofection, the supernatants were collected to infect TZM-bl cells. Infected TZM-bl cells were lysed at 5 dpi for the detection of luciferase activity. cps, counts per second. All data are means ± standard deviations. One representative experiment out of at least two is shown.