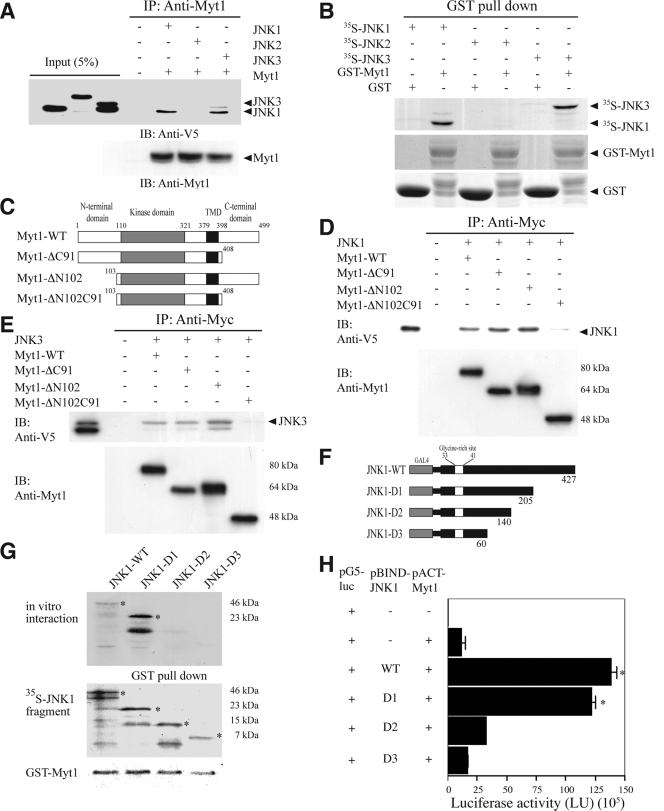
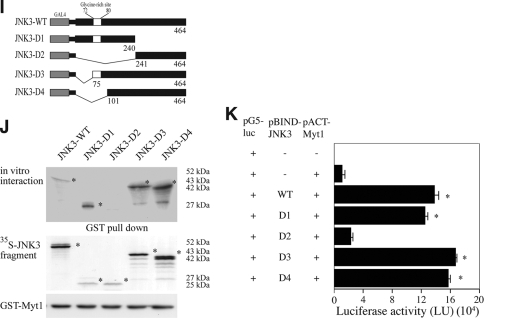
FIG. 1.
The interaction of Myt1 with the JNK proteins. (A) JNK1, JNK2, or JNK3 was coimmunoprecipitated with Myt1. The pcDNA3-V5-JNK1, -JNK2, or -JNK3 plasmid was cotransfected with pcDNA3-myc-Myt1 into HEK293 cells and then cultured for 48 h at 37°C in a 5% CO2 incubator. Cells transfected with the pcDNA3-mock vector served as a negative control. The proteins were extracted as described in Materials and Methods and were used for immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-myc. JNK1, JNK2, and JNK3 were visualized by Western blotting with anti-V5 horseradish peroxidase followed by detection using an ECL detection kit (Amersham Biosciences). (B) In vitro binding with 35S-labeled JNK proteins and a GST-Myt1 fusion protein. The cDNA of each JNK protein was translated in vitro, and then the 35S-JNK proteins were mixed with GST-Myt1 and a pulldown assay was performed. Proteins were visualized by autoradiography. (C) Schematic diagram of full-length (residues 1 to 499) myc-Myt1 (Myt1-WT), the N-terminal fragment (residues 1 to 408) of myc-Myt (Myt1-ΔC91), the C-terminal fragment (residues 103 to 499) of myc-Myt1 (Myt1-ΔN102), or the kinase domain fragment (residues 110 to 321) of myc-Myt1 (Myt1-ΔN102C91). (D and E) The pcDNA3-myc-Myt1-WT, -ΔC91, -ΔN102, or -ΔN102ΔC91 plasmid was transfected with pcDNA3-V5-JNK1 (D) or pcDNA3-V5-JNK3 (E) into HEK293 cells and then cultured for 48 h at 37°C in a 5% CO2 incubator. The cells transfected with the pcDNA3-mock vector served as a negative control. The proteins were extracted as described in Materials and Methods and were used for IP with anti-Myc. JNK1 and JNK3 were visualized by Western blotting with anti-V5 horseradish peroxidase followed by detection using an ECL detection kit (Amersham Biosciences). (F) Schematic diagram of full-length (residues 1 to 427) V5-JNK1 (JNK1-WT) or various deletion mutants of V5-JNK1 (JNK1-D1 [residues 1 to 205], JNK1-D2 [residues 1 to 140], and JNK1-D3 [residues 1 to 60]). (G) In vitro binding with 35S-labeled JNK1-WT or various deletion mutants (JNK1-D1, -D2, or -D3) and a GST-Myt1 fusion protein. The cDNA of JNK1-WT or the deletion mutants (JNK1-D1, -D2, or -D3) was translated in vitro, and then the 35S-labeled JNK1-WT or each respective deletion mutant protein was mixed with GST-Myt1 and a pulldown assay was performed. Proteins were visualized by autoradiography. (H) Ex vivo interaction of pACT-Myt1 with pBIND full-length JNK1 (residues 1 to 427) or each respective deletion mutant. For a negative control, the pACT-Myt1 plasmid was transfected along with the pG5-luc reporter plasmid into NIH 3T3 cells (18,000 cells/ml). The pACT-Myt1 and pBIND-JNK1 plasmids (WT, D1, D2, or D3) were cotransfected with the pG5-luc plasmid to confirm the binding site of Myt1 with JNK1. After a 36-h incubation, the firefly luciferase activity was determined in the cell lysates and normalized against Renilla luciferase activity. All of the experiments were performed at least twice with triplicate samples and are depicted as the means ± standard errors (S.E.). The asterisks indicate a significant increase in activity compared to that for the negative control, pACT-Myt1 only (P < 0.05). The data are shown as relative luciferase activity units (LU) as measured by a Luminoskan Ascent plate reader (Thermo Electron Corp., Helsinki, Finland). (I) Schematic diagram of full-length (residues 1 to 464) V5-JNK3 (JNK1-WT) or various deletion mutants of V5-JNK3 (JNK3-D1 [residues 1 to 240], JNK3-D2 [residues 241 to 464], JNK3-D3 [residues 75 to 464], and JNK3-D4 [residues 101 to 464]). (J) In vitro binding with 35S-labeled JNK3-WT or various deletion mutants (JNK3-D1, -D2, -D3, or -D4) and a GST-Myt1 fusion protein. The cDNA of JNK3-WT or each respective deletion mutant (JNK3-D1, -D2, -D3, or -D4) was translated in vitro; then, the 35S-labeled JNK3-WT or individual deletion mutant protein was mixed with GST-Myt, and a pulldown assay was performed. Proteins were visualized by autoradiography. (K) Ex vivo interaction of pACT-Myt1 with pBIND full-length JNK3 (residues 1 to 464) or each respective deletion mutant. For a negative control, the pACT-Myt1 plasmid was transfected along with the pG5-luc reporter plasmid into NIH 3T3 cells (18,000 cells/ml). The pACT-Myt1 and pBIND-JNK3 plasmids (WT, D1, D2, D3, or D4) were cotransfected with the pG5-luc plasmid to confirm the binding site of Myt1 with JNK3. After a 36-h incubation, firefly luciferase activity was determined in the cell lysates and normalized against Renilla luciferase activity. All of the experiments were performed at least twice with triplicate samples and are depicted as means ± S.E. The asterisks indicate a significant increase in activity compared to that for the negative control, pACT-Myt1 only (P < 0.05). The data are shown as relative luciferase activity units (LU) as measured by a Luminoskan Ascent plate reader (Thermo Electron Corp., Helsinki, Finland).