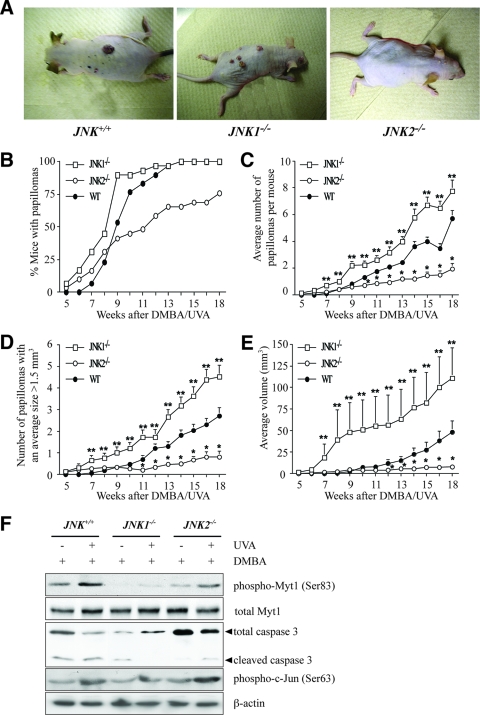
FIG. 6.
The JNK1-mediated phosphorylation of Myt1 inhibits UVA-induced skin tumorigenesis in vivo. (A) External appearance of papillomas. Mice received one topical dose of DMBA (200 nmol in 250 μl acetone) and 2 weeks later were exposed to increasing doses of UVA five times a week (Monday through Friday) as follows: week 1, 4,200 J/m2 or 3.5 min; week 2, 8,400 J/m2 or 7 min; week 3, 16,800 J/m2 or 14 min; week 4, 33,600 J/m2 or 28 min; week 5, 67,200 J/m2 or 56 min; week 6, 100,800 J/m2 or 84 min; and weeks 7 to 18, 144,000 J/m2 or 120 min. Mice were monitored and treated with UVA for 18 weeks after DMBA initiation treatment. (B) Fewer JNK2−/− mice than JNK+/+ or JNK1−/− mice developed papillomas after exposure to UVA. (C) The average numbers of papillomas were significantly different among groups. A single asterisk indicates significantly (P < 0.05) fewer papillomas for JNK2−/− mice than for JNK1−/− or JNK+/+ mice, and double asterisks indicate significantly (P < 0.05) more papillomas for JNK1−/− mice than for JNK2−/− or JNK+/+ mice. Data are expressed as means ± standard errors (S.E.). (D) The average numbers of papillomas of >1.5 mm3 were significantly different among groups. A single asterisk indicates significantly (P < 0.05) fewer papillomas of >1.5 mm3 for JNK2−/− mice than for JNK1−/− or JNK+/+ mice, and double asterisks indicate significantly (P < 0.05) more papillomas of >1.5 mm3 for JNK1−/− mice than for JNK2−/− or JNK+/+ mice. Data are expressed as means ± S.E. (E) Average papilloma volumes were significantly different among groups. A single asterisk indicates significantly (P < 0.05) smaller papillomas for JNK2−/− mice than for JNK1−/− or JNK+/+ mice, and double asterisks indicate significantly (P < 0.05) larger papillomas for JNK1−/− mice than for JNK2−/− or JNK+/+ mice. Data are expressed as means ± S.E. (F) Effect of UVA on the phosphorylation of Myt1 and the activity of caspase-3 in JNK WT and JNK-deficient mice. The dorsal skins from JNK+/+, JNK1−/−, and JNK2−/− mice were biopsied, and the total lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies against the respective proteins. Reproducible results were obtained in three independent experiments, and representative blots are shown.