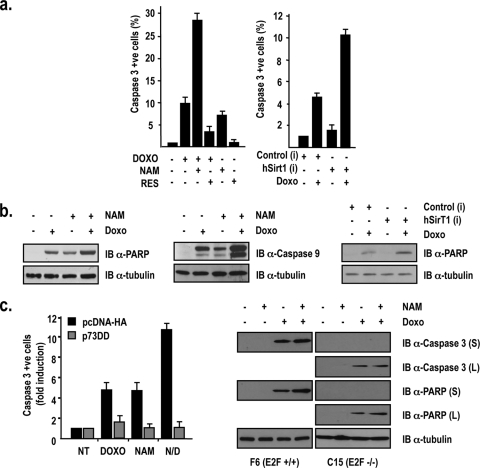
FIG. 4.
hSirT1 regulates p53-independent apoptosis in response to DNA damage. (a) Inhibition of hSirT1 activity potentiates doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in p53 null cells. (Left) SaOs2 cells were exposed for 24 h to doxorubicin (DOXO) (2 μM), NAM (10 mM), and RES (30 μM). (Right) Hep3B cells transfected with control and hSirT1-specific siRNAs were exposed for 24 h to doxorubicin (2 μM). Active caspase 3-positive (apoptotic) cells were identified by indirect immunofluorescence and counted. Results are expressed as induction compared to basal caspase 3 activity measured in untreated cells. (b, left and middle) Whole-cell extracts from untreated and doxorubicin (2 μM)-, NAM (10 mM)-, and doxorubicin-plus-NAM-treated SaOs2 cells were immunoblotted (IB) with anti-cleaved PARP (left) and anti-cleaved caspase 9 (middle). (Right) Hep3B cells were treated as described above (a), and whole-cell extracts were immunoblotted with anti-cleaved PARP. (c) p73 mediates hSirT1 inhibition of p53-independent apoptosis in Hep3B cells exposed to DNA damage. p53 null Hep3B cells transfected with either control PCDNA3-HA vector or the pCDNA3-p73DD-HA expression vector were treated for 24 h with doxorubicin (2 mM), NAM (10 mM), and the combination of NAM plus Doxo (N/D). Active caspase 3-positive (apoptotic) cells were identified by indirect immunofluorescence and counted. Results are expressed as induction compared to that of untreated control and p73DD-transfected cells. The efficiencies of transfection ranged between 75 and 80% among experiments. The numbers of apoptotic cells were consistently between 30 and 40% apoptotic cells in doxorubicin- or NAM-treated cultures and >80% in cells treated with the combination of NAM and doxorubicin. NT, not treated. (Right) Whole extracts from F6 (E2F1+/+) and C15 (E2F1−/−) cells exposed for 24 h to doxorubicin (2 μM), NAM (25 mM), or the combination of doxorubicin and NAM were immunoblotted with anti-cleaved caspase 3 and anti-cleaved PARP. In the case of C15 (E2F1−/−) cells, data for both a short ECL exposure (2 min) and a longer exposure (2 h) are provided.