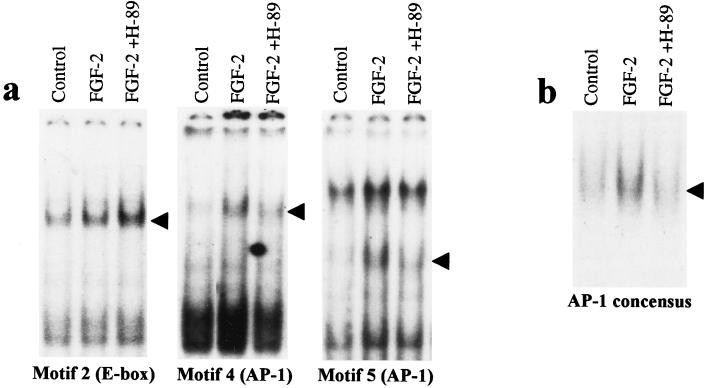
Figure 3.
Inhibition of PKA activity decreases the binding of FGF-2 inducible AP-1 complexes to FiRE. (a) An electrophoretic mobility-shift assay was performed with radiolabeled, double-stranded oligonucleotides encompassing USF-1 binding motif N2 (E-box) and AP-1 binding motifs (N4 and N5) of FiRE. Nuclear extracts from serum-starved NIH 3T3 cells (control), serum-starved cells treated with FGF-2 (10 ng/ml) for 2 hr, or cells treated with 10 μM PKA inhibitor H-89 for 30 min before FGF-2 treatment were used. Arrowheads indicate specific binding described previously (7). (b) Reduction in FGF-2-induced AP-1 binding by PKA inhibition is not restricted to FiRE. Pretreatment with 10 μM H-89 prevented FGF-2-induced AP-1 binding to the AP-1 concensus oligonucleotide containing the TPA (12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate)-responsive element.