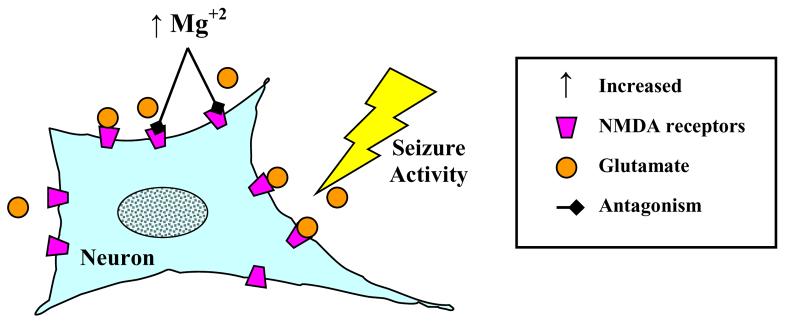
Figure 3. Anticonvulsant Activity of Magnesium Sulfate.
Seizures consist of an excessive release of excitotoxic neurotransmitters including glutamate. Excessive glutamate can activate the N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, leading to massive depolarization of neuronal networks and bursts of action potentials. Magnesium may act to increase the seizure threshold by inhibiting NMDA receptors, thereby limiting the effect of glutamate.