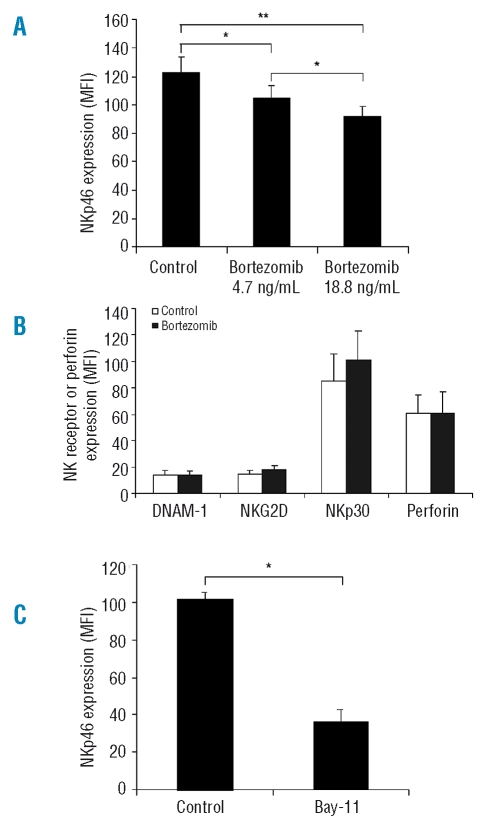
Figure 4.
Bortezomib and Bay 11-7082 downregulate NK cell activating receptor NKp46 expression in resting NK cells. Primary rNK cells treated by bortezomib (4.7 ng/mL or 18.8 ng/mL) or the NF-κB inhibitor, Bay 11-7082 (1.25 μM) for 12h and untreated rNK cells (control) were stained with fluorescence conjugated antibody specific for NKp46 and the expression of NKp46 (mean fluorescence intensity, MFI) was quantified by flow cytometry. (A) Comparison of NKp46 expression (MFI) between bortezomib-treated and untreated rNK cells. The results presented are mean ± SEM (n=3). *p<0.05 and **p<0.02 by Student’s t test. (B) Comparison of cell surface expression of DNAM-1, NKG2D and NKp30, as well as intracellular perforin expression (MFI) between bortezomib (4.7 ng/mL)-treated and untreated rNK cells. Expression of the NK cell activating receptors (DNAM-1, NKG2D and NKp30) and perforin was quantified by flow cytometry as described in the Design and Methods section. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=3). *p<0.01 by Student’s t test. (C) Comparison of NKp46 expression (MFI) between Bay 11-7082-treated and untreated rNK cells.