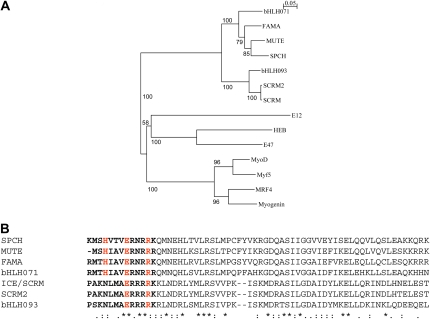
Figure 3.
Phylogeny and comparison of bHLH proteins regulating stomatal development in Arabidopsis. A, Phylogeny of the bHLH proteins that control stomatal development. Myogenic bHLH proteins serve as an outgroup. SPCH, MUTE, and FAMA cluster in the same clade. bHLH093 clusters in the SCRM/SCRM2 clade. The bHLH domains were used to calculate the neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree using ClustalX2 software. Branch lengths are proportional to sequence distance. Bootstrap values are based on 1,000 replicates. The GenBank accession numbers are as follows (in parentheses): bHLH071 (NP_568666), FAMA (Q56YJ8), MUTE (ABI74926), SPCH (ABI26170), bHLH93 (NP_001078801), SCRM2 (ACA63683), SCRM (AAP14668), E12 human (CAC14267), HEB human (NP_996923), E47 human (NP_001129611), MyoD human (CAA40000), Myf5 human (NP_005584), MRF4 human (NP_002460), and myogenin human (NP_002470). B, Sequence comparisons among the bHLH domains. The H-E-R residues are shown in red. The basic region is shown in boldface type. Asterisks indicate identical residues, colons indicate conservative changes, and periods indicate semiconservative changes. Proteins were aligned using the ClustalW2 software.