Figure 1.
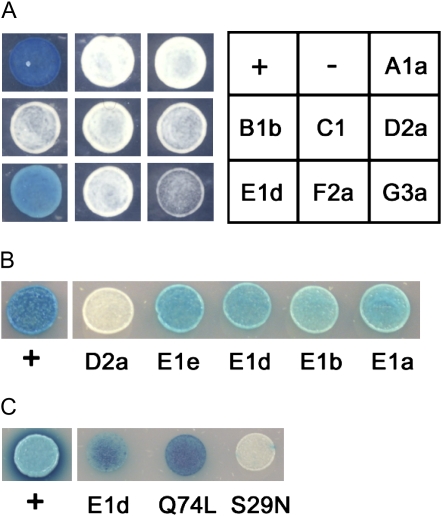
Arabidopsis RabE proteins interact with P. syringae AvrPto in the Y2H system. Interaction is visualized by development of blue color on medium containing X-Gal. Negative control (−) = pNLexA (bait) and pB42AD (prey) vectors; positive control (+) = pLexA-A53 and pB42AD-T. A, AvrPto (in pNLexA) interacts with Arabidopsis RabE1d but not with other members of the Rab superfamily (in pB42AD). B, AvrPto (in pNLexA) interacts with all four tested Arabidopsis RabE proteins (in pB42AD). Yeast expressing AvrPto in pNLexA and RabD2a in pB42AD is shown as a negative control. C, AvrPto (in pB42AD) interacts with RabE1d or RabE1d-Q74L but not with RabE1d-S29N. For this experiment only, wild-type RabE1d and the mutated RabE1d proteins were cloned in the bait vector pGILDA and modified by replacing the two C-terminal conserved Cys residues (sites of geranylgeranylation [Supplemental Fig. S1]) with Gly and Ser to prevent prenylation and membrane association.