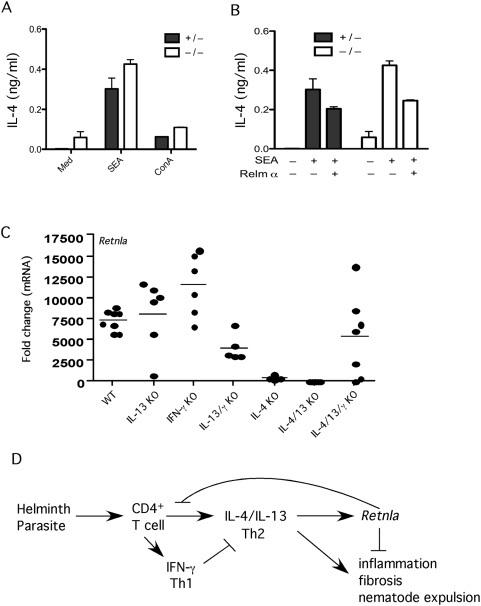
Figure 9. Retnla is induced by IL-4/IL-13 and inhibited by IFN-γ.
(A) Splenocytes were harvested from mice sufficient (HET, +/−) or deficient (KO, −/−) in Retnla 12 days after i.p. sensitization with 5000 viable S. mansoni eggs. Cells were stimulated with media, SEA (25 µg/ml) or ConA (1 µg/ml) in duplicate for 72 h at 37°C at which time supernatants were harvested and tested for IL-4 by ELISA. (B) Separate groups of SEA stimulated cells were also treated with PBS or rRelma (0.5 µg/ml) and examined for IL-4 (bars show Means±SD). (C) WT C57BL/6, IL-13KO, IFN-γ KO, IL-13/IFN-γKO, IL-4KO, IL-4/IL-13KO, and IL-4/IL-13/IFN-γ KO mice were infected with 30–35 S. mansoni cercariae and liver mRNA was isolated on wk 9 post-infection and prepared individually for real-time RT-PCR analysis of Retnla. Gene expression (mean±SEM) is expressed as the fold-increase over naïve WT controls after normalization to HPRT. The results from individual mice are shown. (D) Model depicting the role of Retnla in the regulation of Th2-driven inflammation, fibrosis and immunity to GI nematode infection. Retnla is induced by IL-4 and IL-13 and inhibits the Th2 effector response.