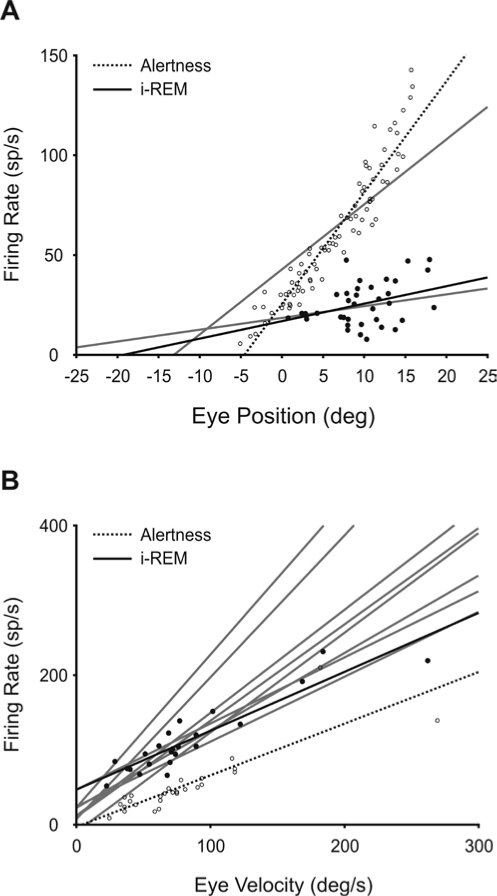
Figure 7.
Codification of eye position and velocity by abducens motoneurons during induced REM sleep. Identified abducens (ABD) motoneurons (n = 9) were recorded during induced REM (i-REM) sleep, and their firing rate was analyzed with respect to the position (A) and velocity (B) of the ipsilateral eye in the horizontal plane. During i-REM sleep, the majority of ABD motoneurons lost their tonic activity, and in those cases in which some tonic activity remained, the correlation of activity with eye position (black dots and regression line in A) was poor with respect to the case of alertness (open circles and dashed line). B. By contrast, the maximum firing discharge of ABD motoneurons correlated with the peak velocity of the eye during rapid eye movements (black dots and regression line), as during alertness (open circles and dashed line). Gray lines correspond to the linear regression lines for each analyzed motoneuron. Parametric and statistical values for each motoneuron are given in Table 1.