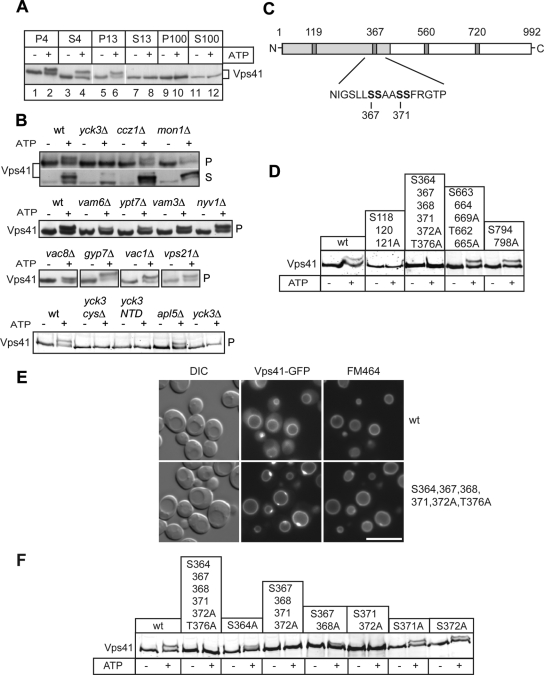
Figure 2.
Identification of the Vps41 phosphorylation site. (A) Phosphorylation of Vps41 occurs on membranes. Yeast cells were separated by subcellular fractionation into a low-speed (P4), a medium-speed (P13), and a high-speed pellet (P100). Pellets and the corresponding supernatants (S4, S13, and S100) were incubated for 60 min in the absence or presence of ATP and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using an anti-Vps41 antiserum. (B) Proteins influencing Vps41 phosphorylation. Membranes (P13) obtained from the indicated yeast deletion mutants were incubated without and with ATP and analyzed as described in A. In the Yck3 cysΔ, the C-terminal CCCFCC sequence has been removed, in the Yck3 NTD (amino acids 1-333), only the N-terminal domain (NTD) of Yck3 is expressed. (C) Potential casein kinase phosphorylation sites in Vps41. The Yck3 target sequence is highlighted. Sites were identified using the online ProSite software (Expasy, http://expasy.org/prosite/). (D) Screening of Vps41 mutants. Cells expressing the indicated Vps41 variants were treated and analyzed as described in A. (E) Localization of GFP-tagged Vps41 mutants. Wild-type and the mutant form of Vps41 were C-terminally GFP-tagged and expressed in cells. The resulting strains were incubated with FM4-64 to label vacuoles and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. Bar, 10 μm. (F) Analysis of the Vps41 phosphorylation site. Membrane fractions of Vps41 alanine mutants were analyzed after ATP incubation as described in A.