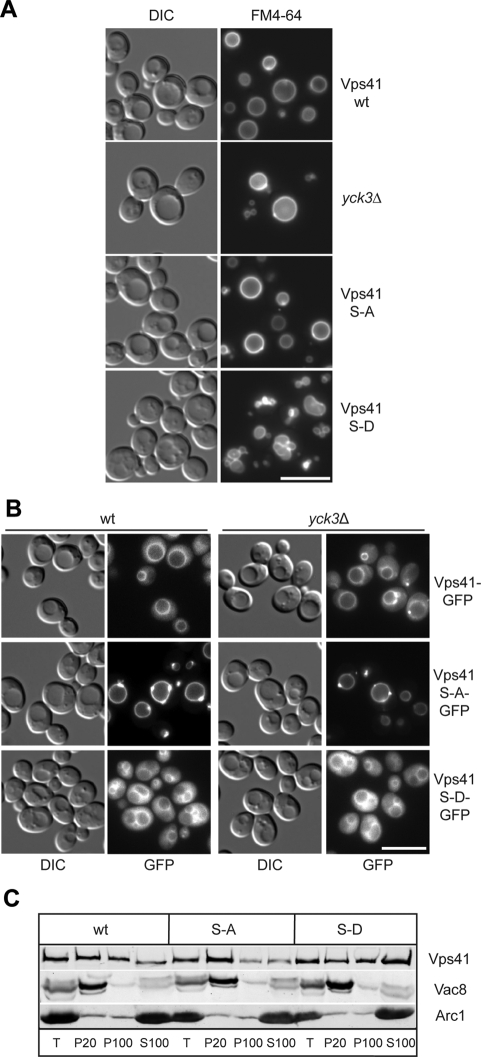
Figure 3.
Phosphorylation of Vps41 modulates its localization and function. (A) Vacuole morphology in Vps41 mutants. Strains expressing the indicated Vps41 mutants were incubated with FM4-64 and analyzed by DIC optics or by fluorescence microscopy. Vps41 S-A carries the S367, 368, 371, 372A point mutations, whereas Vps41 S-D contains the comparable phosphomimetic D mutations. Bar, 10 μm. (B) Localization of Vps41 alanine and aspartate mutants in wild-type and yck3Δ backgrounds. C-terminal GFP-tagged Vps41 was followed by fluorescence microscopy. Bar, 10 μm. (C) Subcellular fractionation of wild-type and Vps41 mutants. Cells expressing C-terminal GFP-tagged Vps41 wild-type or mutant forms were lysed and separated by centrifugation (20,000 × g for 15 min at 4°C) into pellet (P20) and supernatant fractions. The centrifugation of supernatant (100,000 × g for 1 h at 4°C) was performed to isolate pellet (P100) and supernatant (S100) fractions. Proteins within each fraction were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using antibodies against Vps41, Vac8, and the cytosolic protein marker Arc1. T = 50% of total protein used for each separation.