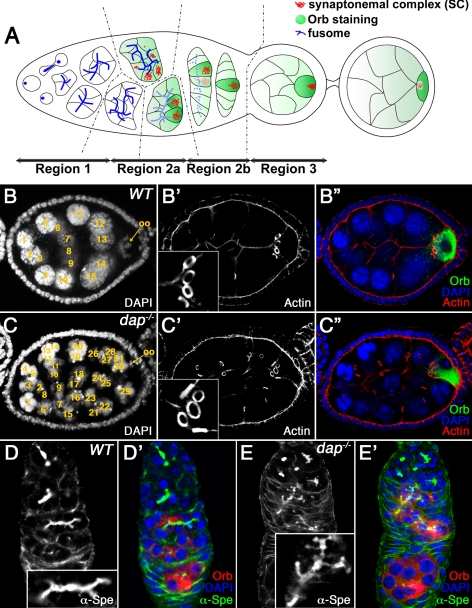
Figure 1.
dap mutants undergo extraovarian cyst divisions. (A) Schematic representation of the germarium. See text for details. The regions of the germarium (1, 2a, 2b, and 3) are indicated at the bottom. Germ cell cyst formation is accompanied by growth of the fusome (blue dots and lines), which forms a branched structure extending through all the ring canals. In midregion 2a, the SC (red) is assembled in the two pro-oocytes, which progress to pachytene. In region 2a, cytoplasmic proteins, such as Orb (green), accumulate in the germline cyst and are progressively restricted to the oocyte. (B) Wild-type and (C) dap−/− mutant egg chambers, stained with DAPI (B, C; B″, C″, blue), rhodamine-conjugated phalloidin (B′, C′; B″, C″, red), and α-Orb antibody (B″, C″, green). The oocyte is indicated by an arrow. Note that the dap−/− mutant oocyte in C″, marked by the α-Orb staining, is surrounded by five ring canals. (D) Wild-type and (E) dap−/− mutant germaria, stained with α-α-Spe (D, E; D′, E′, green) and α-Orb (D′, E′, red) antibodies and DAPI (D′, E′, blue). The inset in D corresponds to a fusome from a 16-cell cyst. Note that the dap−/− mutant fusome in E, inset, is larger and more branched and corresponds to a 32-cell cyst. Insets in D and E are shown at the same magnification.