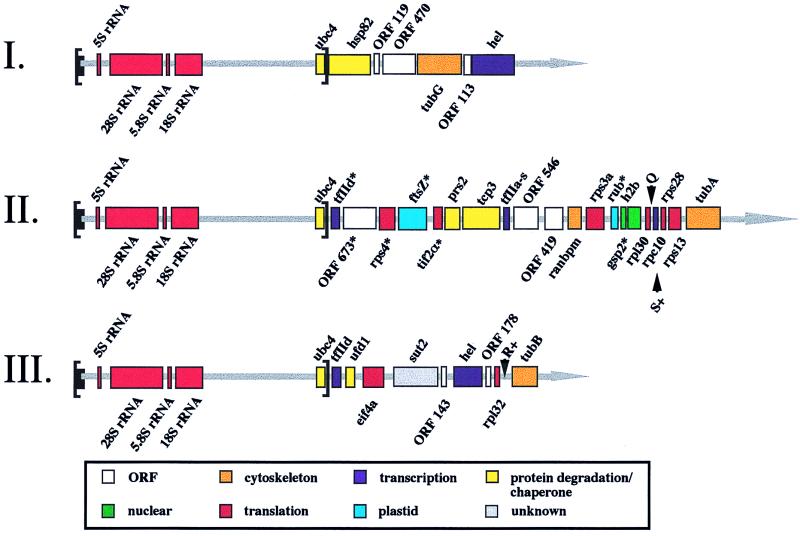
Figure 1.
Physical map of terminal regions of nucleomorph chromosomes I, II, and III of the cryptomonad G. theta. Genes transcribed from the + strand are indicated above the line and those from the − strand below. ubc4, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2; hsp82, heat shock protein 82; tubG, γ-tubulin; hel, RNA helicase; tfIId, transcription initiation factor TFIID; rps4, 40S ribosomal protein S4; ftsZ, cell division protein FtsZ; tif211, hypothetical translational initiation factor 2 α-subunit; prs2, proteasome IOTA subunit; tcp3, T-complex protein 1, TCP-1-γ; tfIIα, transcription initiation factor IIA γ-chain; ranbpm, centrosomal RAN-binding protein; rps3a, 40S ribosomal protein S3a; rub, electron carrier rubredoxin; h2b, histone H2b; gsp2, GTP-binding nuclear protein RAN; rpl30, 60S ribosomal protein L30; rpc10, 7.7-kDa subunit of DNA-directed RNA polymerases I, II and III; rps28, 40S ribosomal protein S28; rps13, 40S ribosomal protein S13; tubA, α-tubulin; ufd, ubiquitin fusion degradation protein; eif4a, eukaryotic initiation factor 4a;. sut2, sulfate permease; rpl32, 60S ribosomal protein L32; tubB, β-tubulin. Arrowheads show positions of tRNAGln(CTG), tRNASer(AGA), and tRNAArg(CCT) and + signs indicate the presence of introns. * mark genes from which cDNAs have been isolated.