Fig. 4.
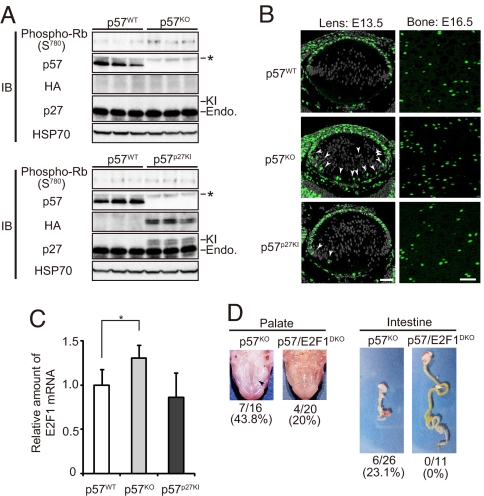
Replacement of the CKI activity of p57 by knocked-in p27. (A) MEFs derived from p57WT, p57KO, or p57p27KI mice were deprived of serum (cultured in the presence of 1% FBS) for 48 h, lysed, and subjected to IP with antibodies to Rb followed by immunoblot analysis with antibodies to phosphorylated Rb (Ser780). Lysates were also subjected directly to immunoblot analysis with antibodies to p57, to HA, to p27, and to HSP70 (loading control). Asterisk indicates nonspecific bands. The band positions for endogenous (Endo.) and knocked-in (KI) p27 are shown. Quantitative data for Rb phosphorylation are shown in Fig. S3B. (B) In situ BrdU incorporation was evaluated for embryos at E13.5 (lens) or E16.5 (zones of proliferative and flattened cells in the humerus). BrdU-positive cells, as well as nuclei stained with Hoechst 33258 (lens only) are green and gray, respectively. Arrowheads indicate ectopic BrdU-labeled cells in the posterior chamber of the lens. (Scale bar, 50 μm.) (C) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of E2F1 expression in the intestine of E18.5 embryos. Normalized data for E2F1 mRNA are expressed relative to the corresponding value for wild-type mice, and are means ± SD (n = 7 or 8). *, P < 0.05 (ANOVA followed by Tukey–Kramer test). (D) Amelioration of cleft palate (arrowhead), and the intestinal defect of p57KO mice in p57/E2F1DKO mice. Penetrance of the defects at E17.5 (palate) and P0 (intestine) is indicated.