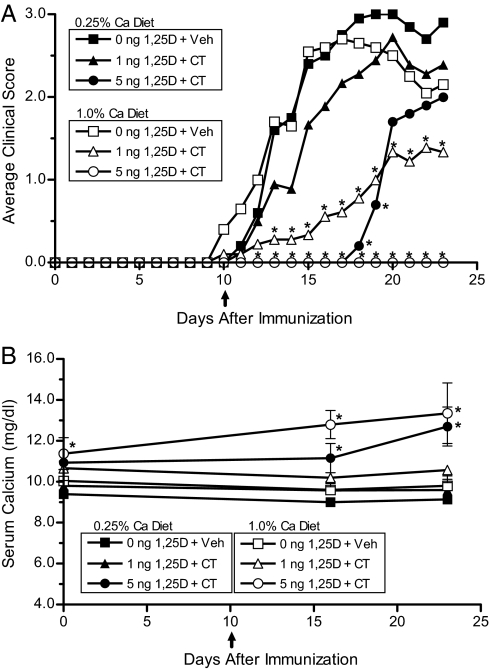
Fig. 4.
Suppression of EAE by the combination of 1,25(OH)2D3 and calcitonin is dependent on dietary calcium. (A) Average clinical scores were determined in mice placed on either a low 0.25% (closed symbols) or a high 1.0% (open symbols) calcium diet treated with selected doses of 1,25(OH)2D3 and CT (n = 5–10). Eight-week-old female C57BL/6J mice were fed 0.25%-calcium- or 1.0%-calcium-purified diet containing 0, 1, or 5 ng of 1,25(OH)2D3 per day. Two weeks after changing the diet, the mice were immunized with MOG35–55. Ten days after immunization, pumps delivering either vehicle or 3 μg/kg per day of salmon CT were implanted s.c. (B) Serum calcium levels (± SD) were measured by atomic absorption spectroscopy at selected time points. ↑, CT treatment initiated and continued for the duration of the experiment. *, P < 0.05 compared with both vehicle-treated groups.