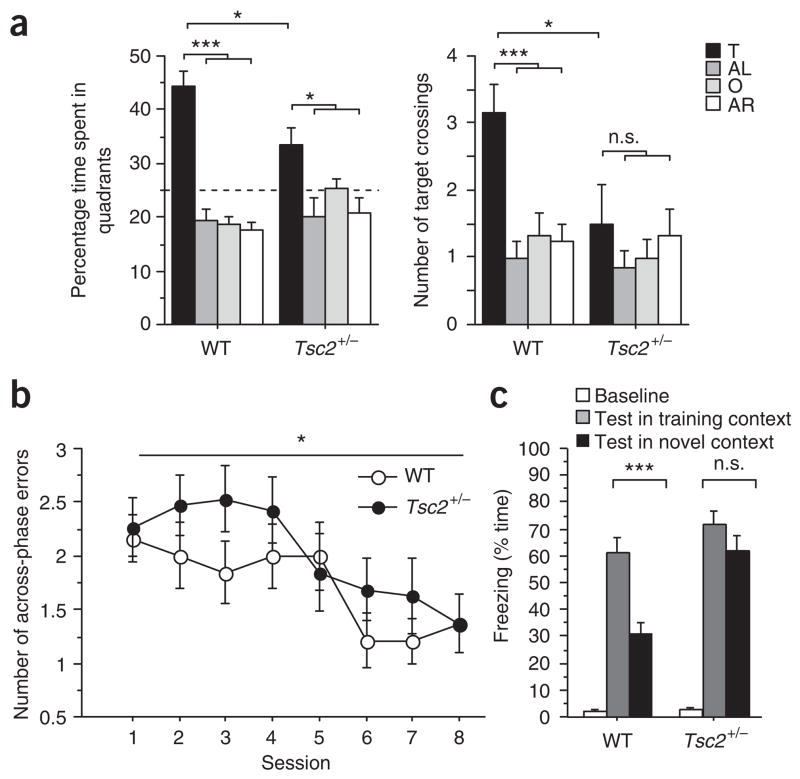
Figure 1.
Tsc2 +/− mice show learning deficits in three hippocampus-dependent tasks. (a) Quadrant occupancy and target crossings during the probe trial given after completion of Morris water maze training (n = 12 mice per genotype; two-way ANOVA for quadrant occupancy with genotype as between-subjects factor and pool quadrant as within-subjects factor, genotype × pool quadrant interaction: F (3,88) = 4.763, P = 0.004; two-way ANOVA for target crossings with genotype as between-subjects factor and pool quadrant as within-subjects factor, effect of genotype: F (1,88) = 4.278, P = 0.0415). Pool quadrants: target quadrant (T), adjacent right (AR), adjacent left (AL), opposite quadrant (O). Dashed line marks chance performance in the Morris water maze. (b) Number of across-phase errors in eight-arm radial maze plotted against training session (n = 19 mice per genotype; one-way repeated-measures ANOVA with genotype as between-subjects factor: F(1,36) = 4.724, P = 0.0364). (c) Context discrimination: freezing scores before shock (baseline) and during the test in the training context (WT mice: n = 11 mice; Tsc2+/− mice: n = 9 mice) or the novel context (WT mice: n = 10 mice; Tsc2+/− mice: n = 9 mice). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, n.s., not significant (P > 0.05). Data represent means ± s.e.m.