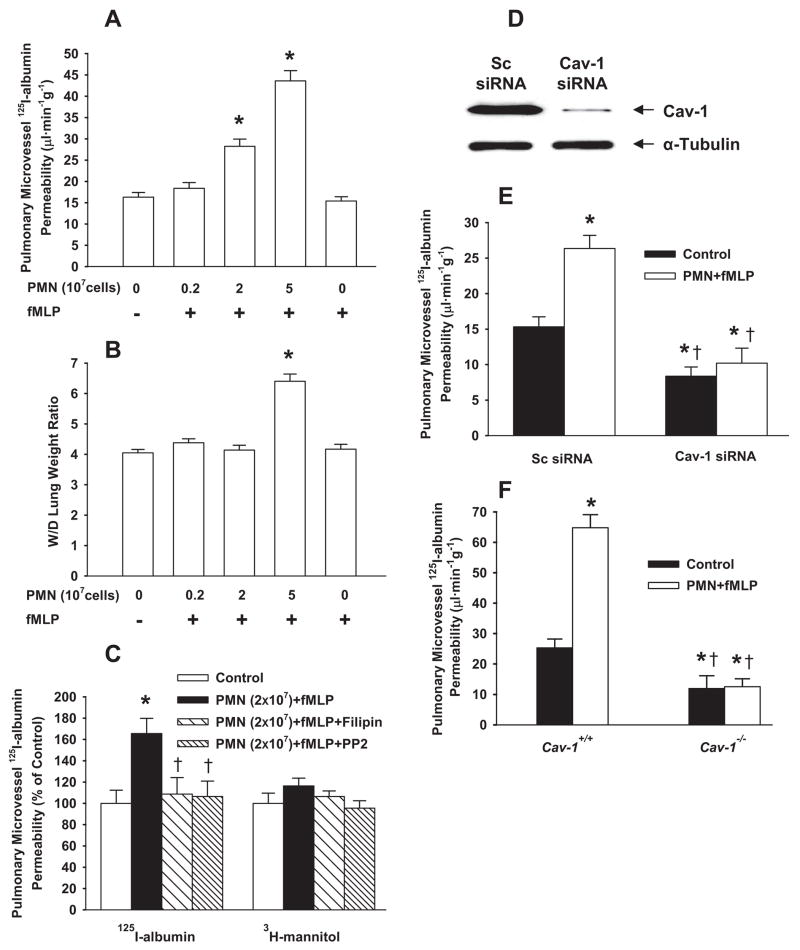
Figure 5.
Activation of PMNs with fMLP induces caveolae-mediated albumin hyperpermeability in rat and mouse lung vessels. After lung perfusion stabilization of 20 minutes, PMNs and fMLP were separately infused in the pulmonary circulation for 30 minutes. A and B, Effect of fMLP-activated rat PMNs (2×106, 2×107, or 5×107 cells) on 125I-albumin PS product (A) and W/D lung weight ratio (B). C, Effects of filipin and PP2 (1 μg/kg) on PMN (2×107 cells) activation-induced changes in 125I-albumin and 3H-mannitol PS products. D and E, Rats were injected with liposomes containing scrambled (Sc) or Cav-1 siRNA in the tail vein. After 48 hours, Western blot analyses of Cav-1 expression (D and supplemental Figure IIA) and pulmonary vascular 125I-albumin PS (E) were assessed. F, Effects of activation of mouse PMNs (2×106 cells) on pulmonary vascular 125I-albumin PS product in Cav-1+/+ and Cav-1−/− mouse lungs. *P<0.05 compared with control groups (without PMNs and fMLP) (A through C and F) or with scrambled siRNA control (E). †P<0.05 compared with PMN (2×107 cells)+fMLP group (C) or with respective groups (E and F).