Figure 4.
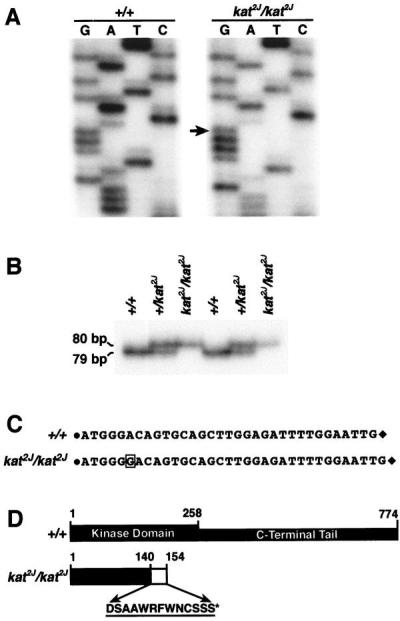
Identification of the kat2J mutation. (A) Sequencing of the RT-PCR product amplified by the primer pair Nek125′ and Nek123′ from +/+ and the KAT2J mutant. The arrow represents the guanosine residue inserted because of the kat2J mutation. The insertion occurs at position +996 nt of the Nek1 transcript. (B) Assay to identify the kat2J mutation in the genomic DNA. Genomic DNAs from known +/+, +/kat2J, and kat2J/kat2J were PCR-amplified with the 16335′ and 16333′ primer pair. The amplified products were resolved on a 6% polyacrylamide gel. The experiment was done on DNAs from two sets of animals. (C) Represents the sequence between the 16335′ and 16333′ primer pair of the genomic PCR fragments obtained from +/+ and kat2J/kat2J animals. The solid circle represents the 16335′ primer, and the solid diamond represents the 16333′ primer. The sequences of the primers are provided in Materials and Methods. The boxed guanosine residue is the insertion resulting from the kat2J mutation. (D) Structural comparison of the wild-type NEK1 protein and the truncated NEK1 protein from the kat2J/kat2J mutant. The amino acids incorporated because of the frame shift are represented by a hatched box and by their single-letter code. The asterisk indicates the position of the premature stop codon.
