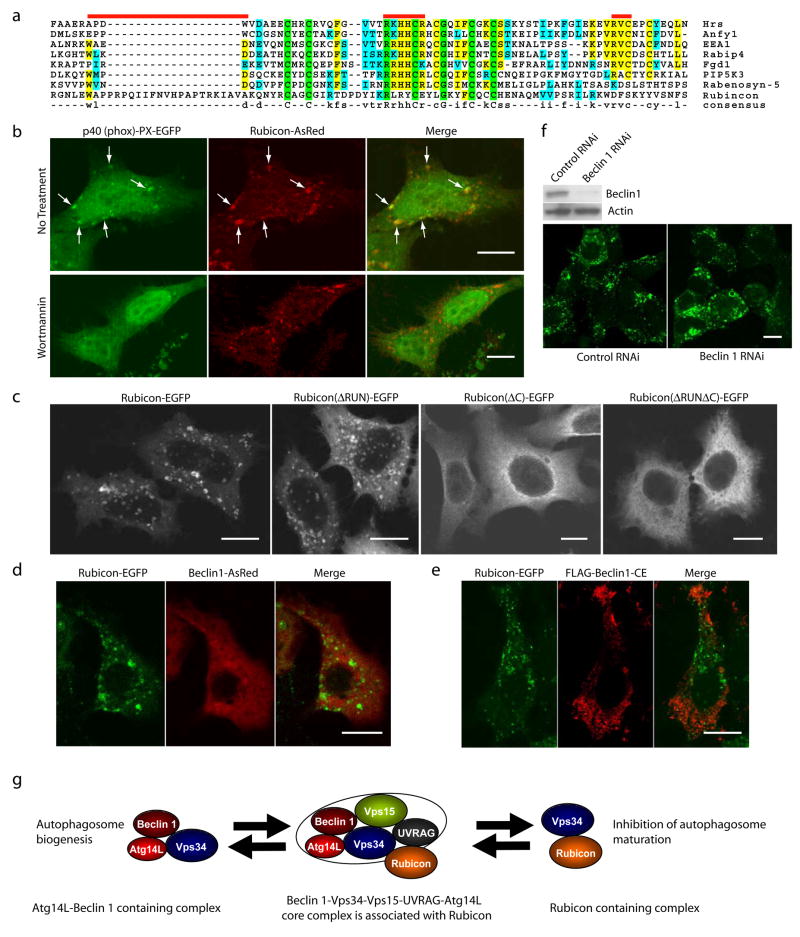
Figure 5. Over-expressed Rubicon is localized on PtdIns(3)P enriched-structures in a Beclin 1-independent manner.
(a) Local sequence alignment between the C-terminal cystein-rich domain of Rubicon and FYVE domains of several known FYVE-containing proteins. Rubicon does not possess the key consensus sequences of a typical FYVE domain, i.e., N-terminal WxxD, central R[R/K]HHCR and C-terminal RVC (indicated by red bars).
(b) Co-localization of the PtdIns(3)P-enriched lipid domain marker p40 (phox)-PX-EGFP (green) and Rubicon-AsRed (red) on large punctate structures (arrows) in the co-transfected HeLa cells (upper panels). Upon short treatment with 75 nM wortmannin (another PI-3K inhibitor) for 1 h, while the PtdIns(3)P-enriched lipid domains disappeared, the Rubicon-AsRed-positive structures was maintained (lower panels). Scale bars: 10 μm.
(c) Subcellular localization of transiently transfected Rubicon-EGFP, Rubicon(ΔRUN)-EGFP, Rubicon(ΔC)-EGFP or Rubicon(ΔRUNΔC)-EGFP in HeLa cells. In contrast to punctate Rubicon-EGFP and Rubicon(ΔRUN)-EGFP, Rubicon(ΔC)-EGFP and Rubicon(ΔRUNΔC)-EGFP were dispersed in cytoplasm. Abbreviations: ΔRUN – RUN domain deletion, ΔC – cysteine-rich domain deletion. Scale bars: 10 μm.
(d-e) Absence of full-length Beclin 1 (d) or Beclin 1-CE mutant (e) (red) on the Rubicon-EGFP-positive structures (green) in the HEK 293 cells stably expressing Rubicon-EGFP. These cells were transiently transfected with either (d) Beclin 1-AsRed or (e) FLAG-Beclin 1-CE (i.e., the FLAG-tagged Beclin 1 mutant containing both CCD and ECD that mediate the Beclin 1-Rubicon interaction as shown in Fig. S3h). Scale bars, 10μm.
(f) The formation of the Rubicon-EGFP-positive structures was not affected by siRNA knocking-down of Beclin 1 in the HEK 293 cells stably expressing Rubicon-EGFP.
(g) A hypothetic model for the Beclin 1-Vps34protein complexes and their functions#. In this model, a core Beclin 1 complex is composed of Vps34/PI-3K, p150/Vps15, Beclin 1, UVRAG and likely substoichiometric Atg14L (indicated by the tight binding and functional connection between Atg14L and Beclin 1). Under physiological conditions, a large Beclin 1-Vps34 complex is formed, including the core complex and Rubicon. This large complex may be reduced to form smaller complexes such as a Atg14L-Beclin 1-containing complex and a Rubicon-containing complex. These smaller complexes are likely the functional units participating in autophagy regulation through modulating the Vps34 lipid kinase activity.