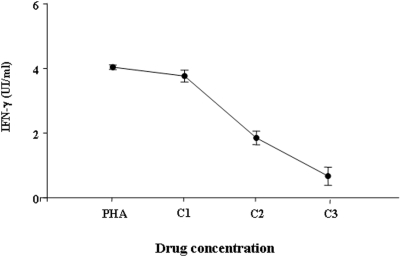
Figure 4. Effect of antituberculous drugs on IFN-γ release in vitro.
The IFN-γ production was evaluated after overnight incubation with the combination of four drugs (rifampicin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, ethambutol) at three different concentrations of solution. C1: INH 5 µg/ml, RIF 7 µg/ml, ETB 5 µg/ml, PZA 40 µg/ml; C2: INH 10 µg/ml, RIF 14 µg/ml, ETB 10 µg/ml, PZA 80 µg/ml; C3: INH 15 µg/ml, RIF 21 µg/ml, ETB 15 µg/ml, PZA 120 µg/ml. Controls wells contained only PHA at 5 µg/ml. The concentrations of IFN-γ produced in the presence of drug concentrations compatible with those achieved in the serum of treated patients (C1) were not significantly different from controls containing only PHA (p = 0,071). In contrast, a significant inhibitory effect was found at more elevated drug concentrations (C2 and C3) (p<0.001 for both). Student's t test was used for statistical analysis.