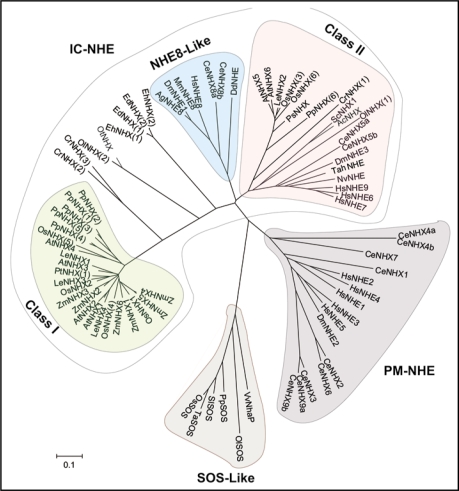
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree of 79 proteins of the monovalent cation proton antiporter CPA1 family. Phylogeneitic relationships were inferred using the Neighbor-Joining method [Saitou N, Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 1987; 4:406–25]. The bootstrap consensus tree inferred from 500 replicates [Felsenstein J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985; 39:783–91], is taken to represent the evolutionary history of the proteins analyzed [Felsenstein J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985; 39:783–91]. Branches corresponding to partitions reproduced in less than 50% bootstrap replicates are collapsed. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Poisson correction method [Zuckerkandl E, Pauling L. Evolutionary divergence and convergence in proteins. In: Bryson V and Vogel HJ, eds. Evolving Genes and Proteins. New York: Academic Press 1965; 97–166] and are in the units of the number of amino acid substitutions per site. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated from the dataset. There were a total of 93 positions in the final dataset. Phylogenetic analyses were conducted in MEGA4 [Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 2007; 24:1596–9]. A list of included sequences is provided in Table 1.