Figure 1.
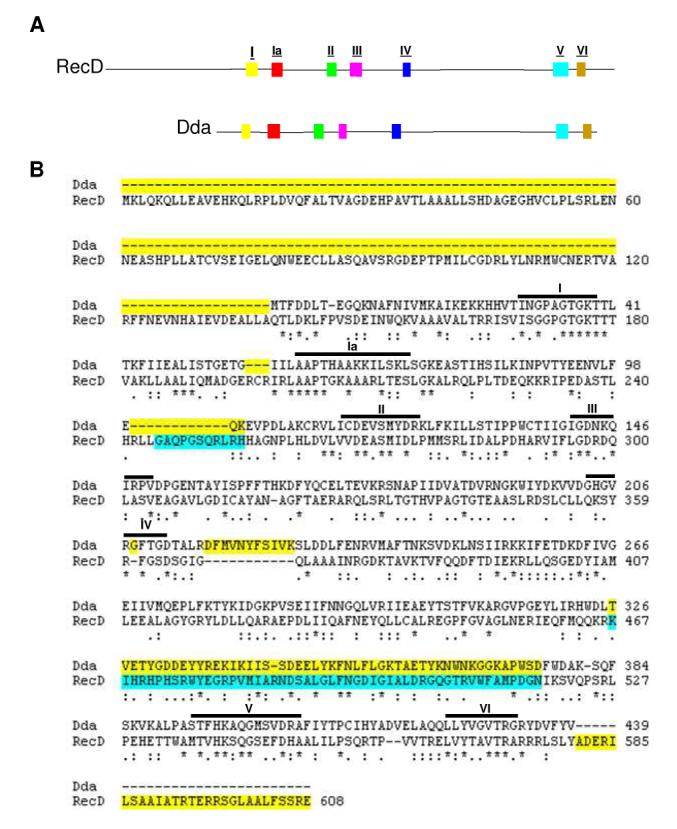
Highly conserved helicase motifs coincide between SF1B helicases Dda and RecD. (A) A side by side comparison of the amino acid sequences of Dda (bottom) and RecD (top) with conserved helicase motifs highlighted. Conserved motifs are as noted in Table 1. (B) Alignment of Dda and RecD used in homology model of Dda. The CLUSTALW program was used to attain an alignment of Dda with RecD. Identical residues are marked with an asterisk while conserved substitutions are marked with two dots and semi-conserved substitutions are marked with one dot. Regions highlighted in yellow were not included in the Dda model. Regions highlighted in blue do not exist in the original E. coli RecD crystal structure.
