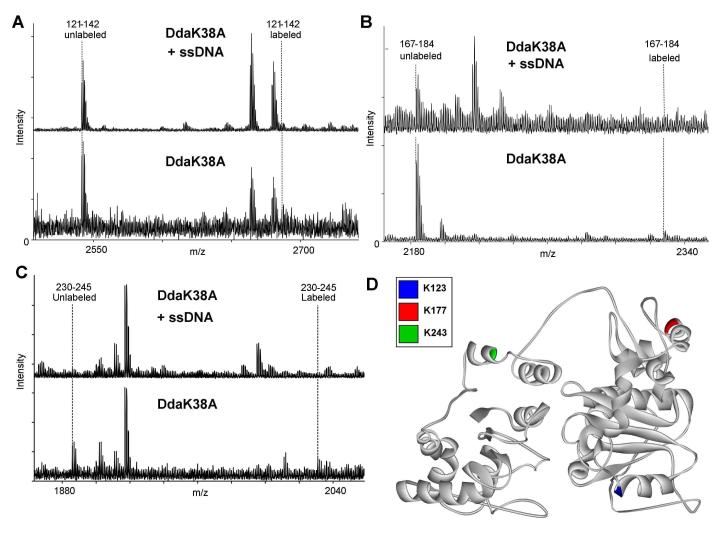
Figure 3.
Identification of amino acid residues that interact with ssDNA by protein footprinting. ssDNA protects Dda from lysine-reactive labeling at three positions: K123, K177 and K243. Dda was exposed to NHS-biotin in the presence or absence of a ssDNA oligonucleotide, (dT)10. (A) Mass spectrometry results indicate an unlabeled 121-142 peptide peak in samples with and without ssDNA, but the labeled 121-142 peptide mass only exists in the samples without ssDNA. This peptide contains two lysines that could be labeled by NHS-Biotin, K123 or K126. Tandem mass spectrometry fragmentation ruled out K126 (Supplementary Figure 4). (B) Mass spectrometry results indicate an unlabeled 167-184 peptide peak in both samples, but the labeled peptide only exists in the samples with no ssDNA. This peptide has one lysine residue, K177. (C) Mass spectrometry results indicate an unlabeled 230-245 peptide peak in both samples, but the labeled peptide only exists in the samples including ssDNA. This peptide has one lysine residue, K243. (D) Representation of protected amino acids in the model. K123 (blue) is located in motif II which has been shown to interact with ssDNA in other helicases. K177 (red) is not located in a conserved helicase motif. K243 (green) is also not located in a conserved helicase motif, but it is located near Motif IV which has been reported to bind ssDNA in other helicases and is in proximity to the ATP hydrolysis pocket in our model. All spectra were matched within an error of 10 ppm.