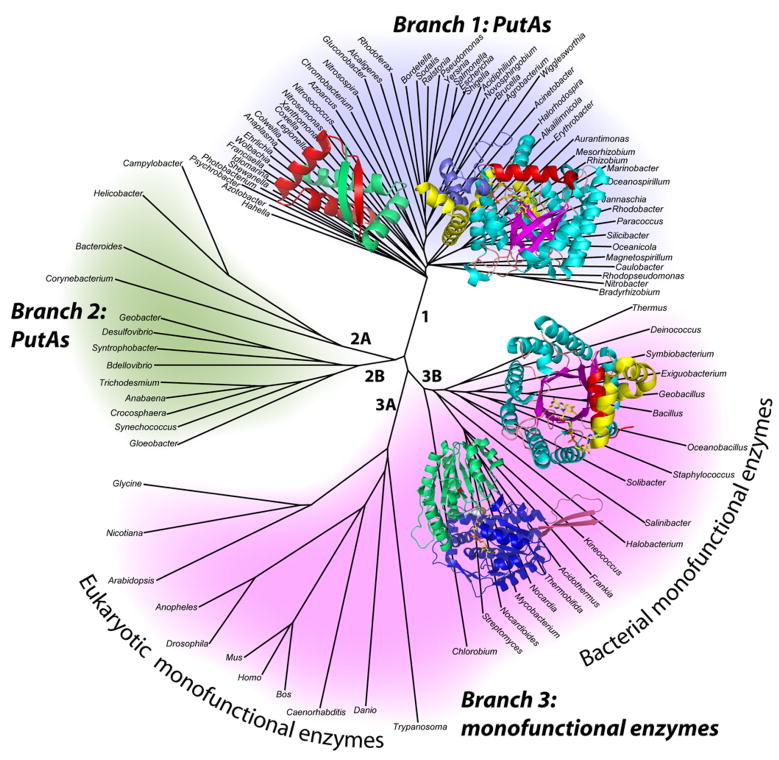
Fig. 2.
Unrooted phylogenetic tree representing the organization of proline catabolic enzymes in bacteria and eukaryotes. The tree has three main branches corresponding to PutAs (branches 1 and 2) and monofunctional enzymes (branch 3). PutAs are found only in bacteria. The monofunctional enzymes appear in both eukaryotes (branch 3A) and bacteria (branch 3B). Structures of proline catabolic proteins and domains are superimposed on their respective branches (clockwise from top left): E. coli PutA DNA-binding domain (branch 1), E. coli PutA PRODH domain (branch 1), T. thermophilus TtPRODH (branch 3B) and T. thermophilus TtP5CDH (branch 3B).