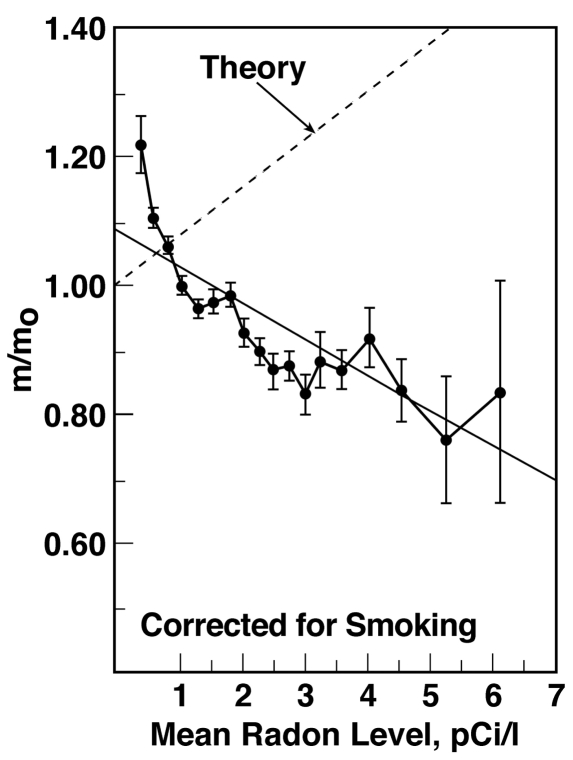
FIGURE 7.
Lung cancer mortality rates compared with mean home radon levels by U.S. county and comparison with linear model by BEIR IV (Cohen 1995)
m/m0 is the ratio of lung cancer mortality rate for residential radon levels to that at 0 level (theoretical), or to that of average residential level of 1.7 picocurie per liter.
Note statistically highly significant increase of lung cancer mortality in counties with very low ambient concentrations of radon, i.e., in radiation deficient portion of Figure 9.