Figure 3. Overview of studies on generation of putative β-cells from HESC.
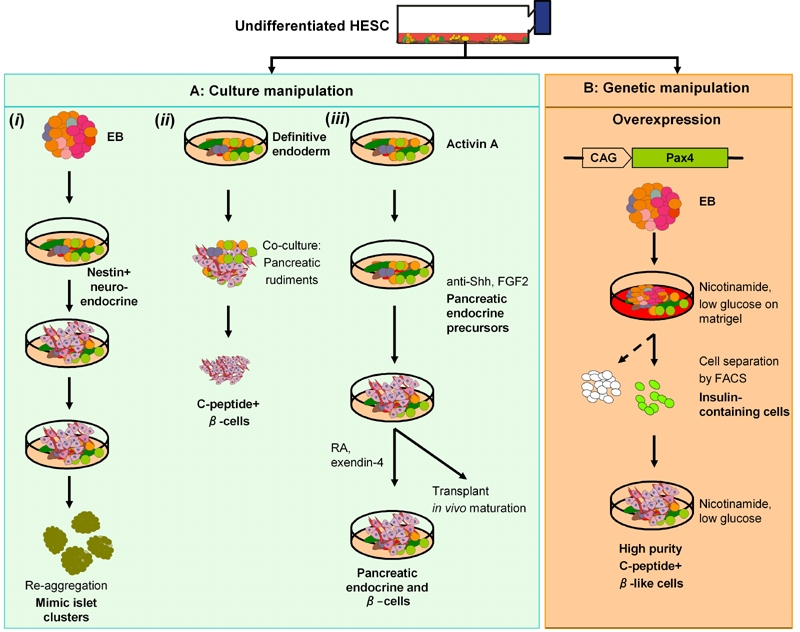
A: Cell culture manipulation. i: Nestin-expressing cells from EB, similar to those differentiated from MESCs gave rise to insulin-immunoreactive cells. Cells were re-aggregated in suspension cultures to yield islet-like clusters consisted of cells expressing pancreatic endocrine hormones. ii: Definitive endoderm (DE) cells differentiated at the edge of HESC colonies were manually picked, co-transplanted with mouse embryonic pancreas further differentiated to β-cells in vivo. iii: A 2D culture generated DE cells by activin A treatment. DE cells responded to hedgehog and Notch inhibitors, giving rise to cells that express pancreas endocrine hormones. Cells transplanted in STZ-induced mice ameliorated hyperglycemia. B: β-like cells were enriched from Pax4-expressing EB and replated on monolayer with nicotinamide and low glucose. A zinc chelating dye was used to isolate insulin-containing cells. These cells went on to form C-peptide-positive cells that responded to β-cell secretagogues. It remains to be determined whether these isolated β-cells rescue hyperglycemia in a mouse model.
