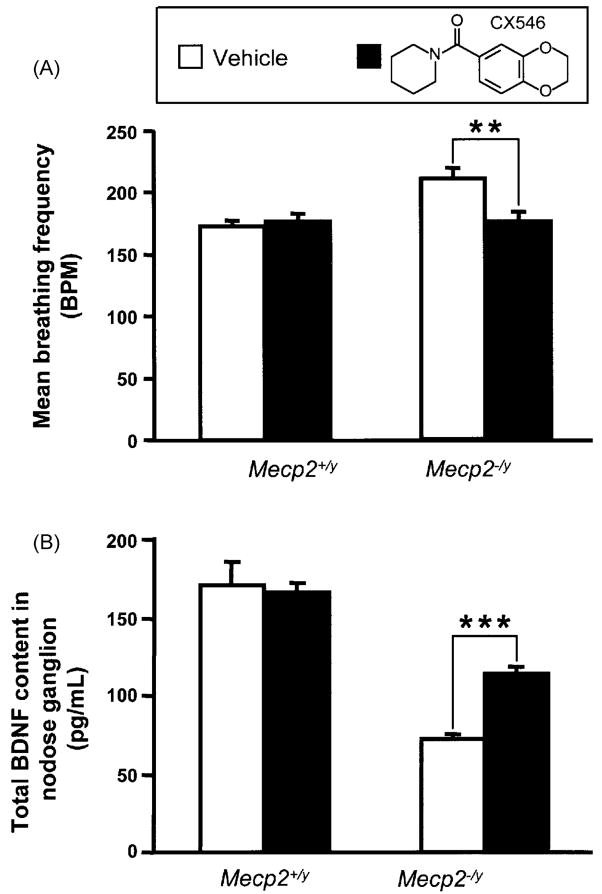
Fig. 2.
Chronic treatment with CX546 restores normal breathing frequency and increases BDNF levels in the nodose ganglia in P35 Mecp2tm1.1Jae null mice. (A) Mean respiratory frequency is higher in vehicle-treated Mecp2 null (−/y) mice compared to wildtype controls (+/y). Following 3-day treatment with CX546 (40 mg/kg, i.p., b.i.d.) respiratory frequency in mutant mice returns to wildtype levels; **p < 0.01, ANOVA I with post hoc Tukey test. (B) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) content is markedly decreased in the nodose ganglia of vehicle-treated Mecp2 null mice compared to wildtype controls (Wang et al., 2006). Treatment of Mecp2 null mice with CX546 results in a significant 42% increase in BDNF levels whereas drug treatment has no effect on nodose BDNF content in wildtype animals; ***p < 0.001, ANOVA I with post hoc Tukey test. Modified from Ogier et al. (2007).