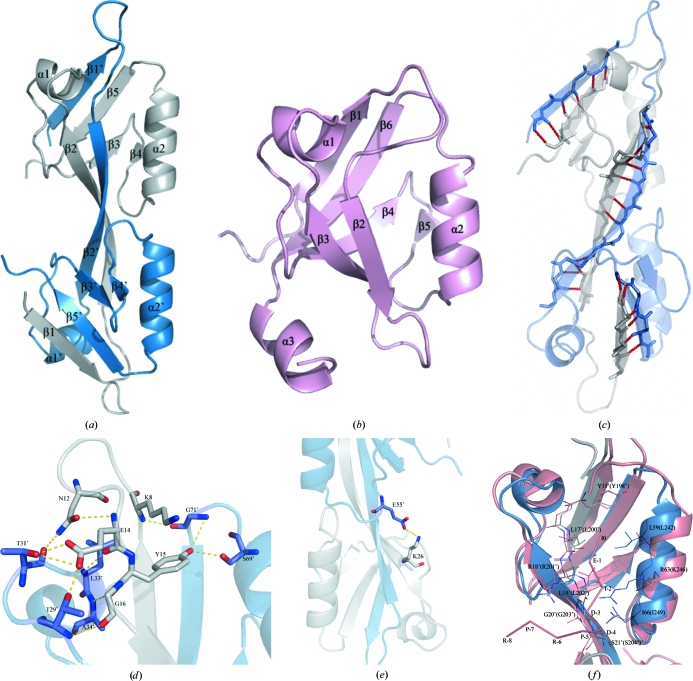
Figure 1.
(a) A ribbon diagram of the domain-swapped dimeric structure. The secondary-structure elements are numbered in order of appearance in the primary structure. One monomer is represented in blue and the other monomer is in grey. (b) The fold of the third PDZ domain from the human DLG protein (PDB code 1pdr; Cabral et al., 1996 ▶), defining the topology of the prototype PDZ domain. (c) Cartoon representation of the interaction between the β1, β2 and β5 strands of the homodimer. The residues that interact via direct hydrogen bonds are shown in stick reprsentation. There are six hydrogen bonds between strands β1 and β5′, 12 hydrogen bonds between strands β2 and β2′ and six hydrogen bonds between strands β1′ and β5. The hydrogen bonds are labelled in red. (d, e) The interactions in the homodimer. Only relevant side chains are shown in this figure for clarity. The broken lines represent hydrogen bonds. (f) Superposition of the putative ligand-binding site of ZO-2 PDZ2 domain (blue and grey) and the corresponding residues that interact with ligands in the structure of the ZO-1 PDZ domain (salmon). The ligand of ZO-1 PDZ2 is also shown (salmon).