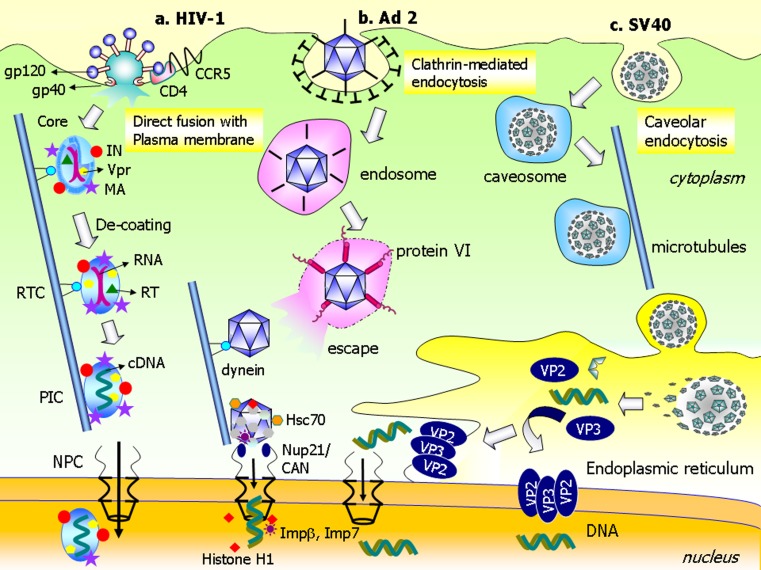
Fig. 1.
Selected mechanisms of intracellular trafficking and nuclear delivery of VIRAL genome. a Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) enters cells via direct fusion with the plasma membrane. gp120 binds to the primary receptor, CD4, and undergoes a conformational change that allows the HIV-1 to associate with its coreceptor, CCR5. This interaction leads to insertion of gp41 into the plasma membrane to mediate fusion. The core is then internalized into the cytoplasm. The capsid core binds dynein and moves along microtubules toward the nucleus. During trafficking, decoating of the capsid results in formation of the reverse transcription complex (RTC). The RNA is converted into complementary DNA by reverse transcriptase (RT) in the preintegration complex (PIC). Matrix protein (MA), integrase (IN), and/or Vpr protein mediate delivery of PIC across the NPC into the nucleus. b After adenovirus type 2 (Ad2) is internalized through clathrin-mediated endocytosis; fiberless Ad2 is entrapped in the endosomes. Protein VI of the Ad capsid causes membrane disintegration and allows Ad to escape the endosomes via detergent-like mechanisms. Ad moves along the microtubules toward the nucleus via interactions with dynein. The Ad capsid is then transported to the NPC where it directly attaches to Nup21/CAN. The Ad–NPC interaction recruits the heat shock protein, Hsc70, and the nuclear histone H1 and H1 import factors, importin β and importin 7. These factors facilitate decoating of Ad and delivery of viral genomic DNA into the nucleus. c SV40 is taken up by cells via caveolar endocytosis and, subsequently, is entrapped in the caveosomes. SV40 traffics to the ER along microtubules. Once inside the ER, the capsid is decoated by ER-resident molecular chaperones. This process leads to dissociation of capsid proteins, in particular VP2 and VP3. These proteins oligomerize and insert into the membrane to facilitate escape of genomic DNA from the ER into the cytoplasm via pore-formation mechanisms. Nuclear delivery of genomic DNA probably occurs in two ways. The genomic DNA is imported to the nucleus from the cytosol after escaping the ER. Another possibility is that the DNA is delivered directly into the nucleus across the ER membrane