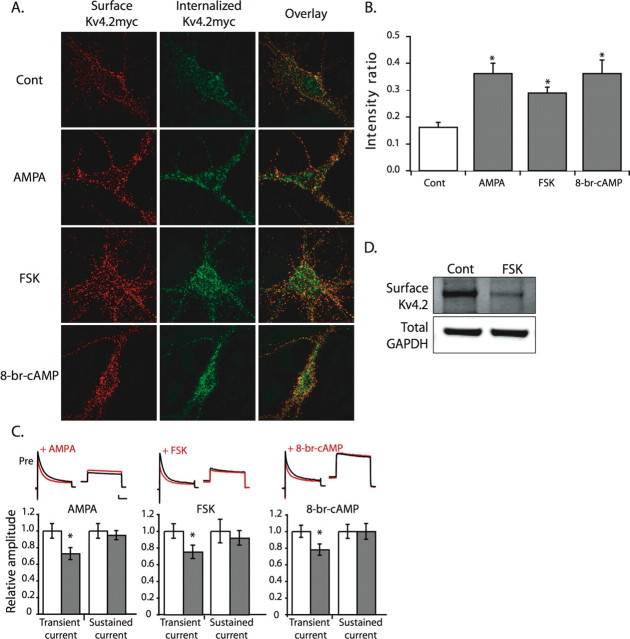
Figure 2.
PKA activation elicits Kv4.2myc internalization in hippocampal neurons. A, Representative images show internalized Kv4.2myc channels (green) and surface-remaining Kv4.2myc channels (red) after AMPA (100 μm), FSK (10 μm), or 8-Br-cAMP (100 μm) treatment. B, Summary plot shows a significant increase in the intensity ratio (green integrated intensity/total integrated intensity) after AMPA (n = 11), FSK (n = 16), or 8-Br-cAMP (n = 10) treatments, relative to control (n = 29). C, In cultured hippocampal neurons, endogenous IA peak amplitude is reduced after AMPA (50 μm; n = 12), FSK (10 μm; n = 14), or 8-Br-cAMP (50 μm; n = 18) treatment, and no changes in sustained current peak amplitudes after any treatment were observed (p > 0.30). Open bars, Pretreatment recordings; gray bars, posttreatment recordings. Calibration: 50 pA, 100 ms. D, The cell-surface biotinylation experiment in acute hippocampal slices demonstrates that surface expression of endogenous Kv4.2 is reduced 37 ± 0.09% after FSK (10 μm; n = 3) treatment compared with control (Cont; n = 3). All data are mean ± SE. *p < 0.05.