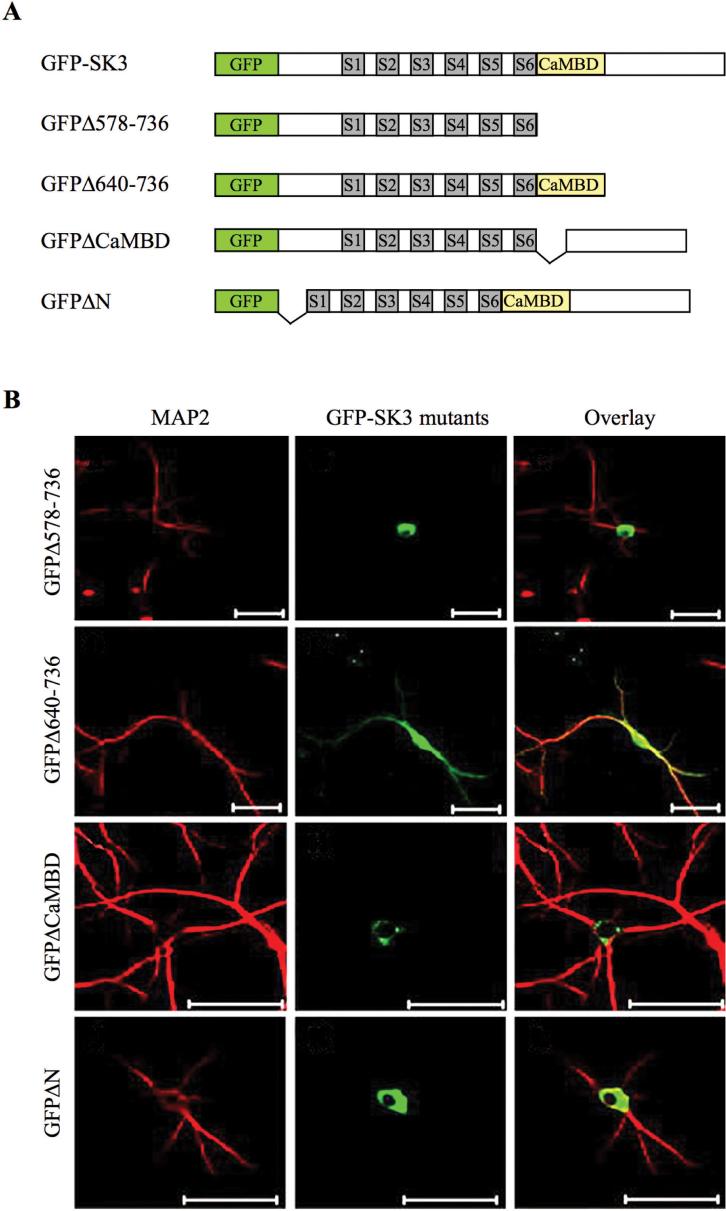
Fig. 4.
Subcellular compartmentalization and trafficking of SK channels. (A) Schematics of green fluorescence protein (GFP)-tagged SK3 and its truncated constructs. Transmembrane domains are indicated as gray boxes, S1-S6, and the calmodulin-binding domain (CaMBD) as a yellow box. (B) Expression and localization of truncated GFP-SK3s in cultured hippocampal neurons stained by anti-MAP2. Confocal images revealed that the N-terminal domain and CaMBD are necessary for proper SK channel transport. Scale bars: 50 μm. (Modified from Decimo and others 2006 with permission.)