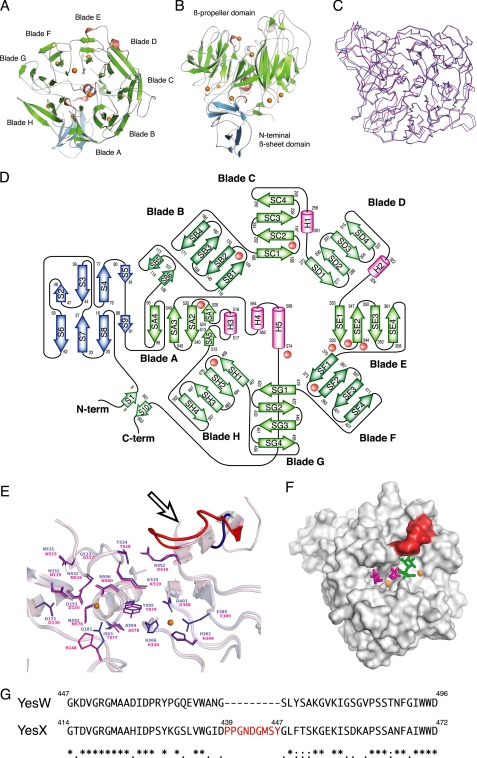
FIGURE 4.
Structure of YesX. A, overall structure. B, image in A is turned by 90° around the x axis. C, superimposition of YesW (blue) and YesX (pink). D, topology diagram. β-Sheets are shown as blue or green arrows, and helices are pink cylinders. The calcium ions are shown as orange balls. E, structural comparison of YesW and YesX in the active site. Residues are colored blue for YesW and pink for YesX. A calcium ion is shown as an orange ball. Loop specific for YesX is colored red and indicated by an arrow. F, comparison in the surface structure among YesX, YesW/GalA-GalA, and YesW/Rha. The loop specific for YesX is colored red. Disaccharide is shown by colored elements: oxygen atom, red; carbon atom, green. The calcium ions are shown as orange balls, and GalA and Rha molecules are shown by green and magenta sticks, respectively. G, amino acid sequence alignment of YesW and YesX (GenPept accession number CAB12524 for YesW and CAB12525 for YesX). Amino acid sequences were aligned using the ClustalW program. Identical residues are denoted by asterisks, strongly conserved residues are denoted by colons, and weakly conserved residues are denoted by periods. The inserted sequence, which corresponds to the loop specific for YesX, is shown in red letters.