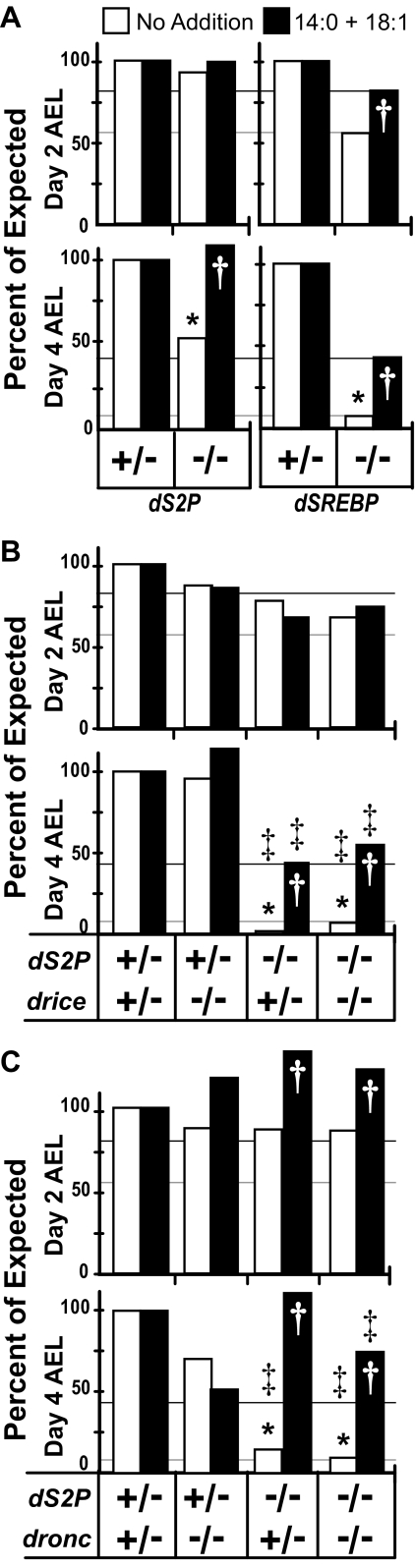
FIGURE 6.
Drice and Dronc are essential for the survival of larvae lacking dS2P. A, virgin females homozygous for dS2P2 were crossed to males heterozygous for dS2P1. Parallel cultures were inoculated with 10 mg/plate of embryos on regular or supplemented medium (14:0 + 18:1). Larvae were scored on day 2 and day 4 AEL. A cross of dSREBP189 heterozygotes served as a control for the efficacy of rescue. B, fly lines harboring mutations in both dS2P1 or dS2P2 and in driceΔ1 were constructed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Virgin females homozygous for dS2P2 and heterozygous for driceΔ1 were crossed to males heterozygous for dS2P1 and driceΔ1. The dS2P homozygous, driceΔ1 heterozygous females were raised on medium supplemented with fatty acids to enable efficient recovery of these flies. Larvae homozygous or heterozygous for driceΔ1 and wild type for dS2P survived equally well under all conditions tested in this experiment. C, crosses of flies doubly mutant for dS2P and dronc51 were conducted as described in B. Horizontal lines corresponding to the value for dSREBP189 larvae under each condition are shown to facilitate comparison (black, supplemented medium; gray, unsupplemented medium). “+” indicates wild type, and “–” indicates null alleles as described above. Note that the values displayed are for whole populations rather than samples. * indicates p < 0.005 for day 2 compared with day 4. † indicates p < 0.005 for supplemented compared with unsupplemented medium. ‡ indicates p < 0.005 for dS2P transheterozygotes compared with dS2P; caspase larvae. A mean of 1057 larvae were scored for each cross and condition (range = 1446 to 751). The results shown are from a single experiment and are representative of three independent replications.