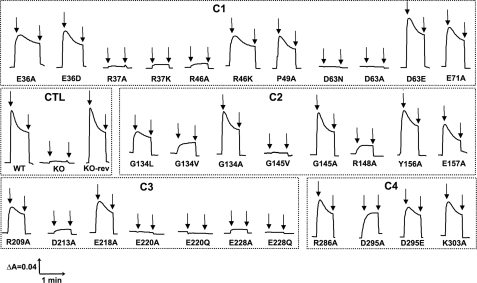
FIGURE 5.
Detection of the membrane potential generated by dNADH oxidation in E. coli NuoH mutants. Membrane vesicles were prepared from each of the constructed mutants, and the membrane potential changes were monitored by the absorbance changes of oxonol VI at 630–603 nm at 37 °C. The assay mixture typically contained 50 mm MOPS (pH 7.3), 10 mm MgCl2, 50 mm KCl, 2 μm oxonol VI, and E. coli membrane samples (330 μg of protein/ml). The first arrow indicates addition of 0.2 mm dNADH and the second arrow indicates addition of 2 μm carbonyl cyanide p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone to the assay mixture. The traces for the mutants are depicted on the basis of their presence in the cytoplasmic loops (C1–C4) along with the controls (CTL). It should be noted that Y156A and E157A are kept along with C2 mutants as they were at the interface. The mutants having the membrane potential similar to the wild-type are not shown.