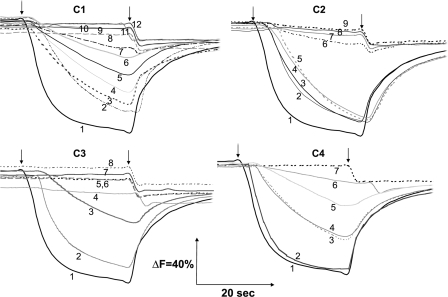
FIGURE 6.
Generation of a pH gradient coupled to dNADH oxidation in E. coli NuoH mutants. Membrane vesicles were prepared from each of the constructed mutants, and the extent of proton translocation was measured by quenching the fluorescence of ACMA at room temperature with an excitation wavelength of 410 nm and emission wavelength of 480 nm. At the time indicated by the arrows, 0.2 mm dNADH (first arrow) or 10 μm carbonyl cyanide p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone (second arrow) was added to the assay mixture containing 50 mm MOPS (pH7.3), 10 mm MgCl2, 50 mm KCl, 2 μm ACMA, and E. coli membrane samples (150 μg of protein/ml). C1 mutants: 1, WT; 2, D63E; 3, P49A; 4, E36D; 5, E36A; 6, E71A; 7, R46K; 8, R37A; 9, R37K; 10, R46A; 11, D63A; 12, D63N. C2 mutants: 1, WT; 2, E157A; 3, G134A; 4, Y156A; 5, G145A; 6, G134L; 7, G134V; 8, G145V; 9, R148A. C3 mutants: 1, WT; 2, E218A; 3, R209A; 4, E220A; 5, E228A; 6, D213A; 7, E220Q; 8, E228Q. C4 mutants: 1, WT; 2, KO-rev; 3, R286A; 4, K303A; 5, D295E; 6, D295A; 7, NuoH KO. Controls (i.e. WT, KO, and KO-rev mutants) are displayed along with the mutants of cytoplasmic loop 4 (C4). As shown are Y156A and E157A in group C2. The mutants that exhibited proton pumping activity akin to the wild-type are not shown.